|
|
|
|
Comparing Shading Modes |
In flat shading mode, the pyramid below is displayed with a sharp edge between adjoining faces. In Gouraud shading mode, however, shading values are interpolated across the edge, and the final appearance is of a curved surface.
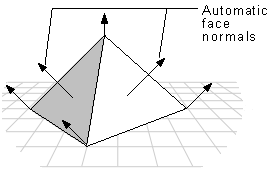
Gouraud shading lights flat surfaces more realistically than flat shading. A face in flat shading mode is a uniform color, but Gouraud shading enables light to fall across a face more correctly. This effect is particularly obvious if there is a nearby point source.
Gouraud shading smooths the sharp edges between polygons that are visible with flat shading. However, it can result in Mach bands. An application can reduce the appearance of Mach bands by increasing the number of polygons in an object, increasing screen resolution, or increasing the color depth of the application.
Gouraud shading can miss some details. One example is shown in the following illustration, in which a spotlight is completely contained within a polygon face.
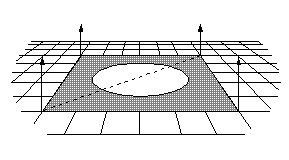
In this case, Gouraud shading, which interpolates between vertices, would miss the spotlight altogether, and the face would be rendered as though the spotlight did not exist.
Send comments about this topic to Microsoft. © Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Feedback? Please provide us with your comments on this topic.
For more help, visit the DirectX Developer Center