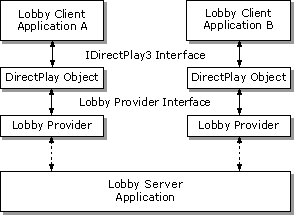
The DirectPlay lobby architecture consists of a client API that all applications, whether they are external lobby clients or applications that have a lobby client built in, use to connect to any DirectPlay-compliant lobby server. This is done through a lobby provider interface that, like a service provider, abstracts the interaction with the lobby server. The author of the lobby server application must write the lobby provider that resides on the client computer. The application calls the standard DirectPlay APIs, and the lobby provider's dynamic-link library (DLL) services these methods by communicating with the lobby server software.
The following diagram illustrates the DirectPlay lobby architecture. Different lobby client applications can connect to the same lobby server through the DirectPlay API.

At the very least, the lobby server must be able to track all the users currently connected to it, organize those players by grouping them, and synchronize the launch of an application session.
The DirectPlay API defines a common level of functionality for all lobby servers. Any generic lobby client application can connect to any generic lobby server and, through the DirectPlay API and the lobby provider architecture, they can interoperate successfully. An application can extend the basic functionality with Send and Receive. A lobby client designed to work with a specific lobby server can implement extended functionality that is not defined by the DirectPlay API.
There is no separate API to communicate with a DirectPlay lobby server. Interaction with a lobby server has been abstracted so that the same IDirectPlay3 interface used to communicate in an application session can be used to communicate with the lobby server. Additional methods and messages have been added to the interface to support the additional functionality that a lobby server requires.
By using the same DirectPlay methods to interact with the lobby server, it is simple to add a lobby client interface to an application, because the same APIs and concepts are being leveraged.