| Microsoft DirectX 8.1 (C++) |
This topic applies to Windows XP Home Edition and Windows XP Professional only.
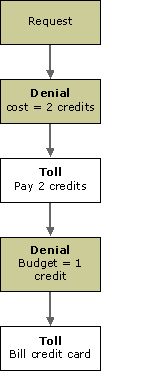
A denial that blocks a request is called a primary denial. A policy can also place a denial on a toll, which blocks the user from paying the toll. This type of denial is called a secondary denial.
For example, suppose that a cable service uses a micro-payment system in which subscribers buy credits or "viewing points," and spend them to view programs. Whenever a subscriber tunes to a program, the policy for that service will create a denial that blocks the request, along with a toll that can be removed by spending a certain number of credits. For example, a particular show might cost 2 credits.
However, suppose the subscriber runs out of credits. In that case, the policy would add a secondary denial to the toll, blocking the user from paying the toll. The secondary denial would have another toll, requiring the user to purchase more credits. To unblock the request, the subscriber would have to pay the secondary toll (purchase credits), followed by the primary toll (spend credits).
The following diagram illustrates this example.
