| Microsoft DirectX 8.1 (Visual Basic) |
In applications that work with 3-D graphics, you can use geometrical transformations to do the following:
You can transform any point into another point by using a 4×4 matrix. In the following example, a matrix is reinterprets the point (x, y, z), producing the new point (x', y', z').
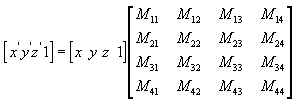
Perform the following operations on (x, y, z) and the matrix to produce the point (x', y', z').

The most common transformations are translation, rotation, and scaling. You can combine the matrices that produce these effects into a single matrix to calculate several transformations at once. For example, you can build a single matrix to translate and rotate a series of points. For more information, see Matrix Concatenation.
Matrices are written in row-column order. A matrix that evenly scales vertices along each axis, known as uniform scaling, is represented by the following matrix using mathematical notation.

In Microsoft® Visual Basic®, Microsoft Direct3D® uses matrices declared as a two-dimensional array, using the D3DMATRIX type. The following example shows how to initialize a variable of type D3DMATRIX to act as a uniform scaling matrix.
' In this example, s is a variable of type Single.
Dim ScaleMatrix As D3DMATRIX
With ScaleMatrix
.m11 = s
.m22 = s
.m33 = s
.m44 = 1
End With