When a menu command is followed by an ellipsis (...), PWB needs more information before executing the command. You enter this information in a dialog box that appears when you choose the command.
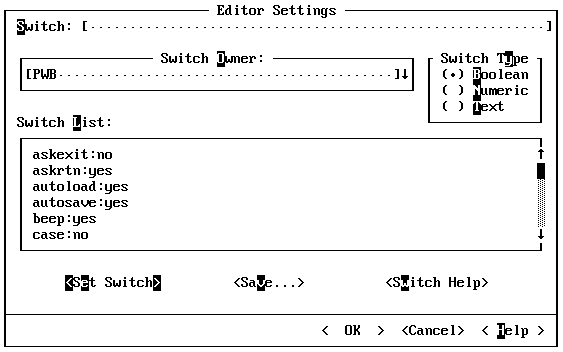
Dialog boxes can contain any of the items in Figure 4.5.

Option Button
A button that you select from a list of mutually exclusive choices. Click the one you want, press its highlighted letter, or use the arrow keys to move among the choices.
Text Box
An area in which you can type text. You can move the cursor within the text box by clicking the location with the mouse or by pressing the LEFT ARROW and RIGHT ARROW keys. You can toggle between insert and overtype mode by pressing the INS key. To select text for deletion, click and drag the mouse over the text or press SHIFT plus an arrow key. Press DEL to delete the text, or type new text to replace the highlighted text.
List Box
A box displaying a list of information (such as the contents of the current disk directory). If the number of items exceeds the visible area, click the scroll bar to move through the list or press PGUP, PGDN, or the arrow keys. You can move to the next item in the list that starts with a particular letter by typing that letter.
Combo Box
The combination of a text box and a drop-down list box. You can type the name of an item in the text box or you can select it from the list.
To open the list, click the highlighted arrow, or press ALT+DOWN ARROW or ALT+UP ARROW. You can then click the item or press the arrow keys to select the item you want. You can also press the first letter of an item to select it. When you have selected an item, click the highlighted arrow or press ALT+DOWN ARROW or ALT+UP ARROW to close the list.
Command Button
A button within angle brackets (< >) that invokes a command. Choose the OK button to accept the current options, or choose the Cancel button to exit the dialog box without changing the current options. Choose the Help button to see Help on the dialog box.
If one of the command buttons in a dialog box is highlighted, press ENTER to execute that command. You can also click a command button to execute that command. If a button contains an ellipsis (...), it indicates that another dialog box will appear when you choose it.
Check Box
An on/off switch. If the box is empty, the option is turned off. If it contains the letter X, the option is turned on. Click the box with the mouse, or press the SPACEBAR or the UP ARROW and DOWN ARROW keys to toggle a check box on and off.
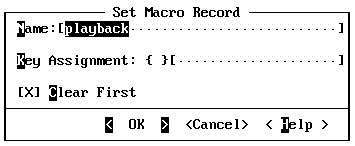
Key Box
A pair of braces ({ }) that allows you to enter a key by pressing the key. The key box is always followed by a text box where you can type the name of the key.
When the cursor is in the key box (between the braces), most keys lose their usual meaning, including ESC, F1, and the dialog box access keys. The key you press is interpreted as the key to be specified. Only TAB, SHIFT+TAB, ENTER, and NUMENTER retain their usual meaning. To specify one of these keys, type the name in the text box.
Clicking a dialog-box item either selects it (a text box, for example) or toggles its value (a check box or option button). You can also move among items with the TAB and SHIFT+TAB keys.
Dialog boxes usually contain access keys, identified by highlighted letters. Pressing an access key is equivalent to clicking that item with the mouse or moving to it by pressing TAB or SHIFT+TAB, and then pressing ENTER. Although some access keys are uppercase and others lowercase, dialog boxes are not case sensitive. Therefore, you can type either an uppercase or a lowercase character.
Note:
When the cursor is in a text box, access keys are interpreted as text. You must press ALT along with the highlighted letter. Pressing ALT is also required in list boxes because typing a letter by itself moves the cursor to the next item that starts with that letter.