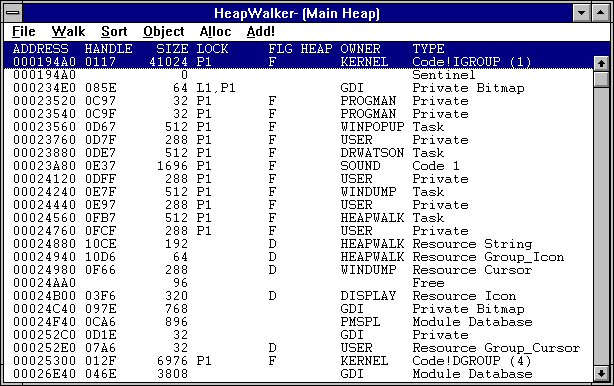
When you start Heap Walker, it scans the global heap and displays information about the allocated and free memory objects.
The following illustration shows a HeapWalker window.

Heap Walker displays the following information about each object:
| Column heading | Information displayed |
| ADDRESS | Address of the memory object (displayed in hexadecimal format). |
| HANDLE | Handle of the memory object (displayed in hexadecimal format). |
| SIZE | Size of the memory object, in bytes (displayed in decimal format). |
| LOCK | Lock count of the object. There are two types of lock counts: page-locked (P) and object-locked (L). Page-locked means that virtual memory will not be used to page the object (pieces of the object will not be written to the swap file); object-locked means the entire object will not be discarded. |
| FLG | D if the object is discardable; F if the object is fixed (not movable or discardable). |
| HEAP | Y if the object has a local heap. |
| OWNER | Owner of the object (name of the module that allocated the object). |
| TYPE | Type of object (code segment, data segment, resource, and so on). Heap Walker searches for symbol files and lists names for segments whenever corresponding symbol files are found. |