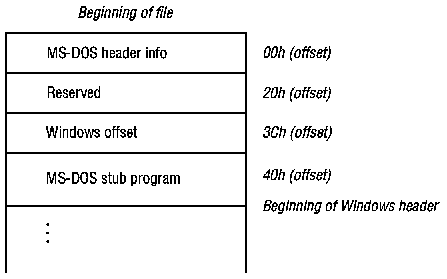
The MS-DOS (old-style) executable-file header contains four distinct parts: a collection of header information (such as the signature word, the file size, and so on), a reserved section, a pointer to a Windows header (if one exists), and a stub program. The following illustration shows the MS-DOS executable-file header:

If the word value at offset 18h is 40h or greater, the word value at 3Ch is an offset to a Windows header.
MS-DOS uses the stub program to display a message if Windows has not been loaded when the user attempts to run a program.
For more information about the MS-DOS executable-file header, see the Microsoft MS-DOS Programmer's Reference (Redmond, Washington: Microsoft Press, 1991).