Visual Basic provides a complete programming environment for creating Windows applications with which you can manipulate the exposed ActiveX objects of other applications. Internally, Visual Basic fully supports Automation dual interfaces.
For the syntax and semantics of the Automation features, see the Visual Basic Help file, Vb.hlp. To see how the Visual Basic statements translate into ActiveX application programming interfaces (APIs), refer to Appendix C, "Information for Visual Basic Programmers."
Note Visual Basic is not necessary to use Automation. It is presented here as an example of a programming tool that supports Automation and is convenient for packaging Automation scripts. Optionally, a different ActiveX client can be used for testing.
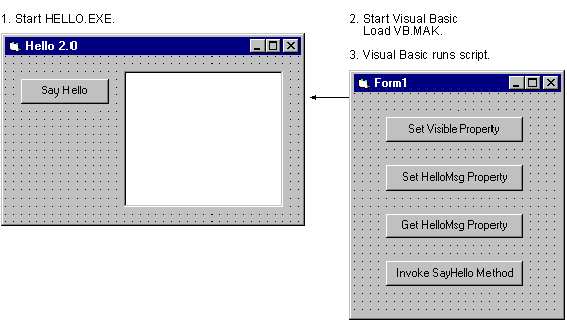
Exposed objects can be called directly from programs written with Visual Basic. The following figure shows how this was done for the sample program Hello.exe.

Dim HelloObj As IHello
Sub Form_Load ( )
Set HelloObj = New Hello.Hello
End Sub
Sub SetVisible_Click ( )
HelloObj.Visible = True
End Sub
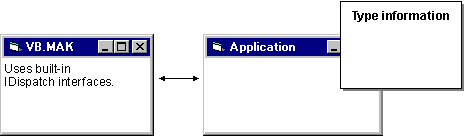
The following figure shows the interfaces you use when accessing exposed objects through Visual Basic.