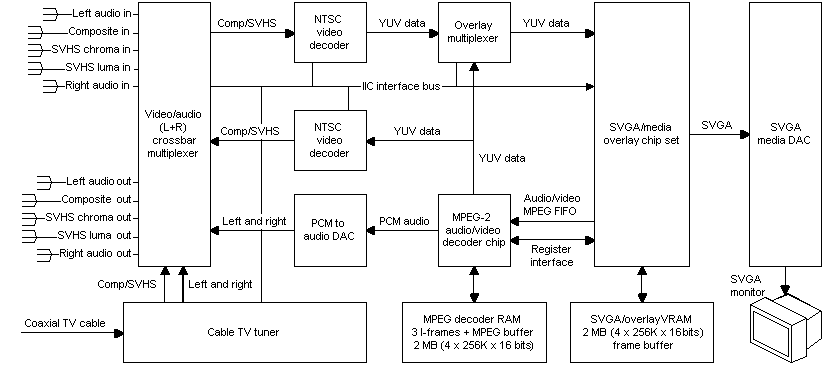
[This is preliminary documentation and subject to change.]
The MPEG decoder is a video and audio decoder capable of handling MPEG-2 main profile and main level data rates (15 megabits per second). The decoder combines MPEG video with standard computer video for display on a super Video Graphics Array (SVGA) monitor. The MPEG decoder has 2 megabytes (MB) RAM for SVGA, including the frame buffer, and another 2 MB RAM for the MPEG decoder itself.
The computer supporting the decoder should also offer a television tuner and base-band, S-video inputs. It should also offer outputs for routing NTSC and PAL signals to and from VCRs, laser disk players, and other video sources. In addition, the computer must provide encoder and decoder circuitry. This circuitry converts NTSC or PAL input signals into digital data in the video frame buffer and converts decoded MPEG video to NTSC or PAL output signals.
The decoder computer must provide separate audio and video outputs that carry audio and video from video sources, as opposed to computer-generated music and sound effects. These separate outputs are provided so that video and its associated audio can be recorded without recording computer-generated music and sound effects. Associated circuitry provides recording control features that can be activated and deactivated under software control. This recording control includes Macrovision encoding of NTSC video generated directly from the MPEG decoder.
The video card portion of the MPEG decoder must meet the criteria of the Plug and Play Framework architecture that is part of the Microsoft® Windows® 95 operating system. Plug and Play provides specific methods for extending the VGA register set and requirements for the appearance of expanded video-card resources on the system bus. For more information on Plug and Play, see Plug and Play Specifications.
The following diagram shows a video system that includes an MPEG decoder. In this illustration, Comp is composite; SVHS is super VHS; IIC is Inter-Integrated Circuit; SVGA is super Video Graphics Array; DAC is digital to analog converter; PCM is Pulse Code Modulated digital input; FIFO is first in, first out; MB is megabytes; K is kilobytes; and VRAM is video RAM.
