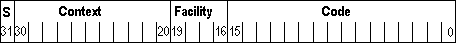
SCODEs on 16-bit platforms are divided into four fields: a severity code, a context field, a facility field, and an error code. The following figure shows the format of an SCODE on a 16-bit platform; the numbers indicate bit positions:
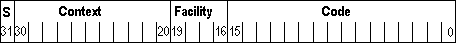
HRESULTs on 32-bit platforms have the following format:

The severity code in the 16-bit SCODE and the high-order bit in the HRESULT indicate whether the return value represents success or failure. If set to zero, SEVERITY_SUCCESS, the value indicates success. If set to 1, SEVERITY_ERROR, it indicates failure.
In the 16-bit version of the SCODE, the context field is reserved; this field does not exist in the 32-bit version. The R, C, N, and r bits are reserved in both.
The facility field in both versions indicates the system service responsible for the error. There are currently five facilities: FACILITY_NULL, FACILITY_ITF, FACILITY_DISPATCH, FACILITY_RPC, and FACILITY_STORAGE. Microsoft allocates new facility codes as they become necessary. Most SCODEs and HRESULTs set the facility field to FACILITY_ITF, indicating an interface method error.
The following table describes the various facility fields:
| Facility | Description |
|---|---|
| FACILITY_NULL | For broadly applicable common status codes such as S_OK. This facility code has a value of zero. |
| FACILITY_ITF | For most status codes returned from interface methods, value is defined by the interface. That is, two SCODEs or HRESULTs with exactly the same 32-bit value returned from two different interfaces might have different meanings. This facility has a value of 4. |
| FACILITY_DISPATCH | For late-binding IDispatch interface errors. This facility has a value of 2. |
| FACILITY_RPC | For status codes returned from remote procedure calls. This facility has a value of 1. |
| FACILITY_STORAGE | For status codes returned from IStorage or IStream method calls relating to structured storage. Status codes whose code (lower 16 bits) value is in the range of DOS error codes (that is, less than 256) have the same meaning as the corresponding DOS error. This facility has a value of 3. |
| FACILITY_WINDOWS | Used for additional error codes from Microsoft-defined interfaces. |
| FACILITY_WIN32 | Used to provide a means of handling error codes from functions in the Win32 API as an HRESULT. Error codes in 16-bit OLE that duplicated Win32 error codes have also been changed to FACILITY_WIN32. |
The code field is a unique number that is assigned to represent the error or warning.
By convention, HRESULTs generally have names in the following format:
Facility_Severity_Reason
where Facility is either the facility name or some other distinguishing identifier; Severity is a single letter, S or E, that indicates the whether the function call succeeded (S) or failed (E); and, Reason is an identifier that describes the meaning of the code. For example, the status code STG_E_FILENOTFOUND indicates a storage-related error has occurred; specifically, a requested file does not exist. Status codes from FACILITY_NULL omit the Facility_ prefix.
Error codes are defined within the context of an interface implementation. Once defined, success codes cannot be changed or new success codes added. However, new failure codes can be written since they generally only provide hints at what might have gone wrong. Microsoft reserves the right to define new failure codes (but not success codes) for the interfaces described in FACILITY_ITF or in new facilities.