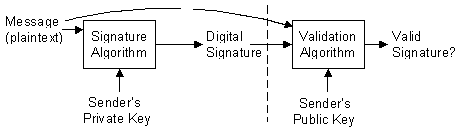
Digital signatures can be used when a message is distributed in plaintext form, and the recipients should be able to verify that the message has not been tampered with by any unauthorized individual. Signing a message does not alter the message, it simply generates a digital signature string that is bundled with the message or transmitted separately.
Digital signatures can be generated using public-key signature algorithms where the transmitting party private key, used to generate the signature, is sent in an e-mail message. Upon receipt of the message, the recipient uses the distinct public key to validate the signature. Because only the signer's public key (received by the recepient in an earlier e-mail) can be used to validate the signature, the digital signature is proof that the message sender's identity is authentic. This process is shown in the following illustration.
