A proxy address is the address by which a Microsoft Exchange Server recipient object is recognized in a foreign mail system. Proxy addresses are required not just for users, but for all recipient objects such as custom recipients, distribution lists, and public folders.
Each Microsoft Exchange Server recipient object will have several proxy addresses — at least one for each foreign address type known to the system. The proxy addresses for each foreign address type are created by a DLL provided with the Addr-Type directory object when the address type is installed.
The following table shows three proxy addresses associated with the native Microsoft Exchange Server user Pat Parkes. Each proxy address is prefixed with its address type. Mail originating in a foreign messaging system is addressed to Microsoft Exchange Server recipients by using the proxy address that corresponds to the foreign system. For example, Internet users address mail to PatParkes@microsoft.com, and when Pat Parkes sends mail to the Internet, it appears to come from PatParkes@microsoft.com.
| Address type | Address |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Exchange Server | EX:/o=microsoft/ou=sales/cn=PatParkes |
| SMTP proxy | SMTP:PatParkes@microsoft.com |
| MS Mail proxy | MS:microsoft/sales/PatParkes |
| X.400 proxy | X400:c=US;a= ;p=Microsoft;s=Parkes;g=Pat |
Users can have primary and secondary proxy addresses. The primary proxy address for a user is the one used when sending mail to the foreign system. The secondary proxy addresses are used when receiving mail from the foreign system. On outgoing messages, the primary proxy address is used as the sender’s address. On incoming messages, the recipient listed in the message is matched against the secondary proxy addresses in the Microsoft Exchange Server directory to find the proper recipient object for the message.
A user has only one primary proxy address but might have multiple secondary addresses. For example, if two companies merge and give new e-mail addresses to all their employees, secondary proxy addresses might be used so that employees can receive mail at both their old and new e-mail addresses. By maintaining the old e-mail addresses as secondary proxy addresses, incoming mail can be addressed to either the old or new address. Outgoing mail is always addressed using the primary proxy address.
A gateway should be able to generate proxy addresses for most types of recipient objects—user mailboxes, custom recipients, and distribution lists, and public folders. It does not need to generate proxy addresses for one-off addresses.
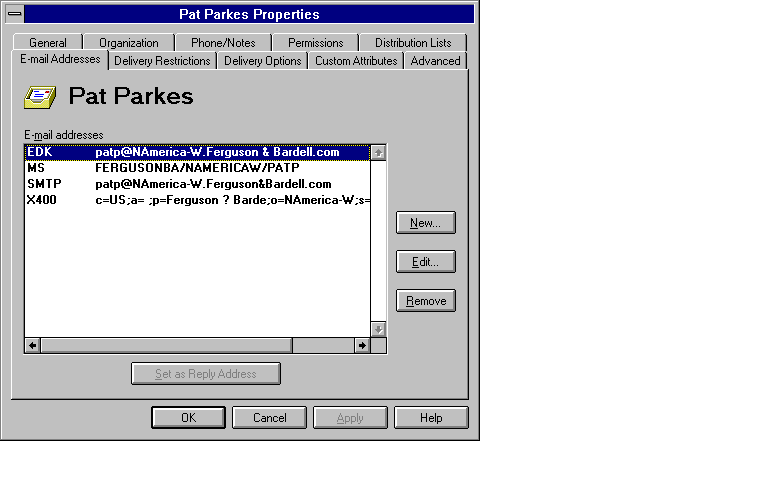
Note The term proxy address is equivalent to the term e-mail address used in the Microsoft Exchange Server Administrator program documentation. To view the proxy addresses for a Microsoft Exchange Server user, click the E-mail Addresses tab on the user’s property sheet. The following figure shows typical proxy addresses.

Proxy addresses