All messages submitted to SMBAGENT are placed in the Inbox folder by the message transfer agent (MTA). SMBAGENT receives notification of each new message from Microsoft Exchange Server through MAPI. When notification is received, the Inbox is searched for new messages. SMBAGENT also implements a polling mechanism that checks the Inbox, even if it has not received notifications. This polling allows messages to be found if problems such as server outages have prevented notification. The default polling frequency is set to one minute, but this can be modified by SMBADMIN. The value NONE turns polling off.
Commands such as JOIN or LEAVE cause SMBAGENT to update information in the existing introduction message for the appropriate topic. Other commands, such as POST, cause the mail agent to generate a message for storage in one of the topic subfolders.
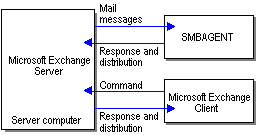
The relationship between SMBAGENT, Microsoft Exchange Server, and a Microsoft Exchange Client is shown in the following figure.

SMBAGENT application architecture
This figure shows Microsoft Exchange Server and SMBAGENT on a single server computer. SMBAGENT uses MAPI to communicate with Microsoft Exchange Server and send and receive information. Microsoft Exchange Client users send commands to SMBAGENT by sending mail messages.
When a message arrives at the SMBAGENT mailbox on Microsoft Exchange Server, SMBAGENT reads the message's Subject property to determine which command to execute. SMBAGENT responds by posting mail messages to Microsoft Exchange Server, which forwards the messages to appropriate recipients.
A user who registers interest in a topic becomes a member of that topic. As messages from members are received, SMBAGENT archives them according to their discussion topic. SMBAGENT can also connect to and store postings in public folders.
The Sample Mailbox Agent will return a General Error message when an attempt is made to create a new topic with an Intro message that includes a link.