The IIS metabase keys correspond to the elements of IIS and each key contains properties that affect the configuration of its associated element. Each node in the metabase structure is called a key and may contain one or more IIS configuration values, called metabase properties. The metabase is organized in a hierarchical structure that mirrors the structure of your IIS installation. Most of the IIS configuration keys and values stored in the system registry for previous versions of IIS are now stored as properties in the metabase. New keys and values have been added for finer and more flexible control of IIS. The structure of the metabase facilitates different settings of a property for different keys. For example, the MaxBandwidth property setting can be a different value for each server.
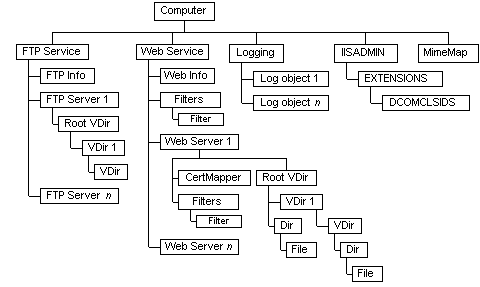
The general structure of IIS is shown in the following figure. Your system's structure may include more or fewer elements depending on your installation choices. Metabase keys associated with IIS elements are addressed by their paths within the metabase. See Key Names and Paths.

The top level metabase key, Computer, contains properties such as MaxBandwidth that affect the overall execution of IIS on your computer. Two keys directly subordinate to the top level key are associated with FTP services and Web services, respectively, and contain properties that affect all FTP servers and all Web servers. Other keys directly subordinate to the top level key contain properties that affect logging and MIME mappings. The IISADMIN key is used to record DCOM extensions to IIS.
Keys directly subordinate to the FTP service key are associated with individual FTP servers and contain properties specific to each FTP server. A key subordinate to each FTP server key is associated with the root virtual directory for that server. Other keys are added below the root virtual directory key as you add virtual directories to your FTP servers. Each of these keys contains properties that affect the operation or configuration of the associated virtual directory. The Info key, directly subordinate to the FTP Service key, also contains some properties associated with the FTP service.
Keys subordinate to the Web service key are associated with individual Web servers, their root virtual directories, subordinate virtual directories, and disk directories and files. A key directly subordinate to the Web service key affects the configuration of filters used by Web service operations. The Info key, directly subordinate to the Web Service key, also contains some properties associated with the Web service.
Keys can also contain references to objects that can be used by the IIS Admin Objects. For example, the CertMapper key contains no metabase properties but does provide access to the IIsCertMapper object and its methods for mapping certificates.