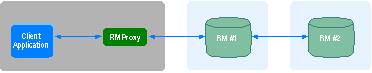
Some resource managers may choose to propagate MS DTC transactions from one OLE Transactions-compliant resource manager to another.
Resource Manager-to-Resource Manager Transaction Propagation

Transaction propagation from resource manager to resource manager is useful when a stored procedure in one database invokes a remote stored procedure in another database. It is also useful when a distributed update, insert, or delete alters data controlled by two or more resource managers. Finally, it is useful if a resource manager permits forwarding of updates to another type of resource manager. For example, a relational database might update a database table and then forward an insert to a transaction-protected queuing system.
Microsoft SQL Server is an example of a resource manager that propagates transactions from resource manager to resource manager. When a SQL Server stored procedure calls a remote stored procedure, SQL Server automatically propagates the MS DTC transaction from the calling SQL Server to the called SQL Server. If the called stored procedure invokes yet another remote stored procedure, the transaction is propagated to it also. This ensures that all databases remain consistent.
If a resource manager encounters an error while propagating a transaction, it normally aborts the entire transaction. In the example above, if resource manager RM #1 cannot propagate the transaction to resource manager RM #2, it will abort the transaction. This might occur if the network connection between the two systems fails. When the transaction is aborted, all work done on behalf of the transaction is undone.