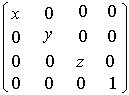
The glScaled and glScalef functions multiply the current matrix by a general scaling matrix.
void glScaled(
GLdouble x,
GLdouble y,
GLdouble z
);
void glScalef(
GLfloat x,
GLfloat y,
GLfloat z
);
The glScale function produces a general scaling along the x, y, and z axes. The three arguments indicate the desired scale factors along each of the three axes. The resulting matrix is
The current matrix (see glMatrixMode) is multiplied by this scale matrix, with the product replacing the current matrix. That is, if M is the current matrix and S is the scale matrix, then M is replaced with M·S.
If the matrix mode is either GL_MODELVIEW or GL_PROJECTION, all objects drawn after glScale is called are scaled. Use glPushMatrix and glPopMatrix to save and restore the unscaled coordinate system.
If scale factors other than 1.0 are applied to the modelview matrix and lighting is enabled, automatic normalization of normals should probably also be enabled (glEnable and glDisable with argument GL_NORMALIZE).
The following functions retrieve information related to glScale:
glGet with argument GL_MATRIX_MODE
glGet with argument GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX
glGet with argument GL_PROJECTION_MATRIX
glGet with argument GL_TEXTURE_MATRIX
The following are the error codes generated and their conditions.
| Error Code | Condition |
|---|---|
| GL_INVALID_OPERATION | glScale was called between a call to glBegin and the corresponding call to glEnd. |
Windows NT: Use version 3.5 and later.
Windows: Use Windows 95 and later.
Windows CE: Unsupported.
Header: Declared in gl.h.
Import Library: Link with opengl32.lib.
glBegin, glEnd, glMatrixMode, glMultMatrix, glPushMatrix, glRotate, glTranslate