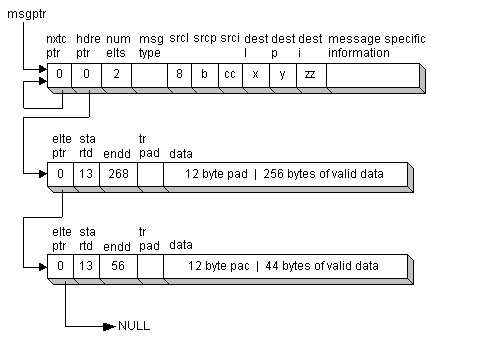
A message always contains fixed-format header information such as a message type and addressing information. It can also contain other header information specific to a particular message type (such as the message subtype) and an indefinite amount of extra data.
Messages are saved in buffers that consist of one header and zero or more elements:
Buffer headers and elements are regarded as contiguous (8-bit) byte sequences. Messages of any length can be built by chaining sufficient elements to a header.
The following figure illustrates a typical message with two elements. The individual fields in the header and elements are explained in the following topics.
