A Base and its components (that is, an SNA Server executable program) is called a locality. The SNA Server system therefore consists of one or more communicating localities (all the running SNA Server executable programs within the LAN Manager domain). For each SNA Server system, there is a central configuration file. In addition, each SNA Server machine maintains configuration information about the SNALinks it supports (see Diagnostics).
In a system such as SNA Server, where the number of localities and their types are not configured in advance, the relationships between the localities are set up dynamically as individual localities come and go. Localities that can enter and leave a system in this way are called dynamic localities.
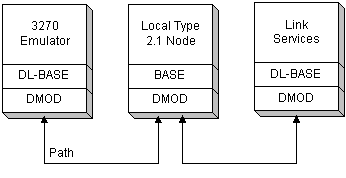
Dynamic localities communicate using the DMOD (dynamic access module) component, which provides the communications facilities needed to pass messages between the Bases. This is illustrated in the following figure.

This diagram shows a system consisting of three dynamic localities. Dynamic localities can enter or leave this system at any time.