Refer to Incoming Call Support for details of the role an SNALink plays in node identification.
When XIDs are exchanged, there are two mechanisms for identifying the remote station:
The presence of signaling information depends on the type of the SNALink. For instance, there is no signaling information over an SDLC link, but there is signaling information over X.25 and 802.2. The SNALink passes signaling information to the local node on the Request-Open-Station message by appending it after the XID.
If signaling information is present, the local node checks it against the configured value in the Dial-Digits record of the SNA Server configuration file. For incoming call support, this allows the local node to determine the connection that is to be activated. See Incoming Call Support for a fuller description of incoming calls.
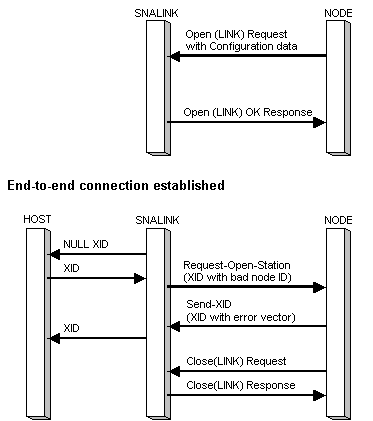
If there is no signaling information, the local node compares the control point name on the received XID with the remote CP name in the configuration.
If the remote station is identified correctly, XID exchange proceeds as detailed in Activating a Peer Connection. However, if there is a mismatch, the local node sends an XID (in the Send-XID message) containing an error vector followed by a Close(LINK) Request, as shown in the following figure.
