 To use setup to install an additional language on the server
To use setup to install an additional language on the serverMicrosoft SQL Server is available in both United States English and localized versions. All versions include system messages in United States English. Localized versions also include system messages that have been translated into another language (such as German or French).
When you install a localized version of SQL Server, the setup program automatically installs the localized messages and date/time formats for you. If you have more than one alternate language, you can use the setup program to install the localized messages and date/time formats for each language. The setup program lets you determine the default language. DB-Library™ - based applications use the country settings established using the International application in the Windows NT Control Panel. For additional information, see the descriptions of dbconvert and dbinit in Microsoft SQL Server Programming DB-Library for C.
ODBC-based applications use code page translation, This is defined from the ODBC Control Panel application, while setting up the options for the ODBC SQL Server driver.
You can add additional languages at any time simply by running setup¾it is not necessary to perform a full installation to add a language. You can find out which languages have been installed by using the sp_helplanguage System Stored Procedure (described in the Microsoft SQL Server Transact-SQL Reference.
You change the default language for SQL Server by using the setup program or the SET LANGUAGE statement. You set the default language for a specific user using SQL Enterprise Manager or by using the sp_defaultlanguage System Stored Procedure (described in the Microsoft SQL Server Transact-SQL Reference).
 To use setup to install an additional language on the server
To use setup to install an additional language on the server
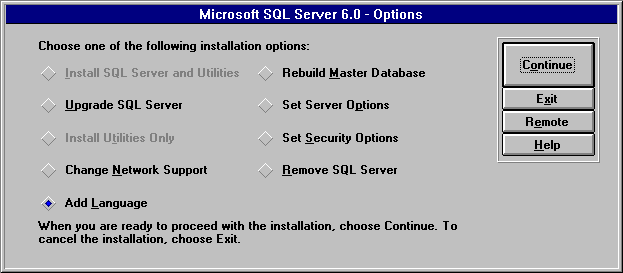
The Select Language dialog box appears.
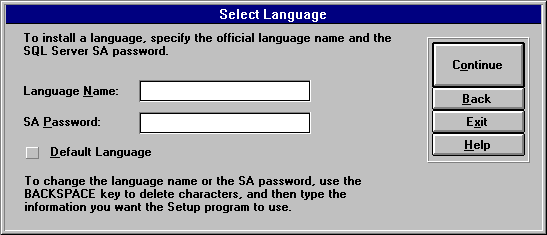
The SQL Server Path dialog box appears.
For more information on adding a language, see the setup program's online Help.