 To set up server connections on a Windows NT- or Windows 95-based client
To set up server connections on a Windows NT- or Windows 95-based clientBy default, SQL Server client/server connections are established over named pipes using dynamic server names that require no special configuration on the clients. (You can connect using named pipes over any Microsoft-supplied transport, including NWLink IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, and NetBEUI.)
If you need to connect to a SQL Server using another network transport that is not the default, or if you need to connect to a SQL Server that is listening on an alternate named pipe, you must first add the connection information to the appropriate configuration file on the client.
For Windows NT-, Windows 95, and Windows-based clients, you set up server connections by using the SQL Client Configuration Utility, which updates the appropriate information on the client.
Note Advanced connection information can be shared by both DB-Library and ODBC applications. If the server name specified in the ODBC SQL Server dialog box matches a server name configured using the Advanced tab of the SQL Client Configuration Utility, and if the ODBC network address and network library remain set to default, then the connection information shown in the Advanced tab of the SQL Client Configuration Utility is used by ODBC.
 To set up server connections on a Windows NT- or Windows 95-based client
To set up server connections on a Windows NT- or Windows 95-based clientThe SQL Client Configuration Utility window appears.
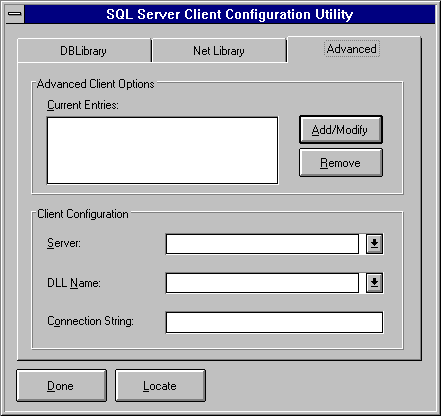
Or you can type the name of a Net-Library DLL to use for the connection. (Do not type the ".DLL" filename extension.) Net-Library DLL choices are listed in "Setting the Default Net-Library," earlier in this chapter.
For information on the type of connection information that can be entered in this box for each Net-Library, see Network Client Connections.
 To set up server connections on a Windows-based client
To set up server connections on a Windows-based client

The SQL Client Configuration Utility window appears.
The Advanced Client Options dialog box appears.
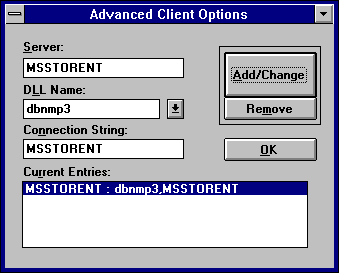
Net-Library DLL choices are listed in "Setting the Default Net-Library," earlier in this chapter.
11.1.4.68,1433
For information on the type of connection information that can be entered in this box for each Net-Library, see Network Client Connections.
For MS-DOS - based clients, you set up server connections by setting an environment variable. Typically, this involves changing the client's AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
For MS-DOS - based clients using the named pipes Net-Library (DBNMPIPE.EXE), you can set up a connection to use alternate pipe names by assigning an environment variable equal to the fully qualified pipe name. For example:
set servername = \\myserver\pipe\altpipe\query
You must set this variable before you load the Net-Library TSR. Other Net-Libraries for MS-DOS supplied by Microsoft do not support server aliases using environment variables. For Net-Libraries supplied by companies other than Microsoft, see your package documentation.