 To add a database device
To add a database deviceYou add a database device by using SQL Enterprise Manager or the DISK INIT statement. The following procedure assumes that you are using SQL Enterprise Manager. For information about using the DISK INIT statement, see the Microsoft SQL Server Transact-SQL Reference.
Note If you are planning to use hardware- or operating system-based striping to hold large databases, set up the stripe sets prior to defining devices. For information see Chapter 7, Managing Drives.
 To add a database device
To add a database device
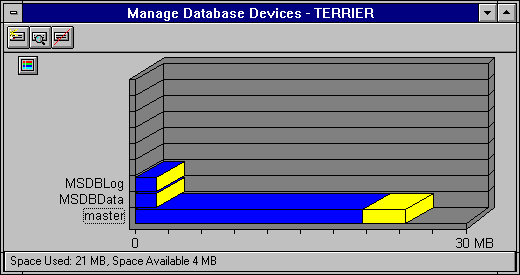
The Manage Database Devices window appears.
The New Database Device window appears.
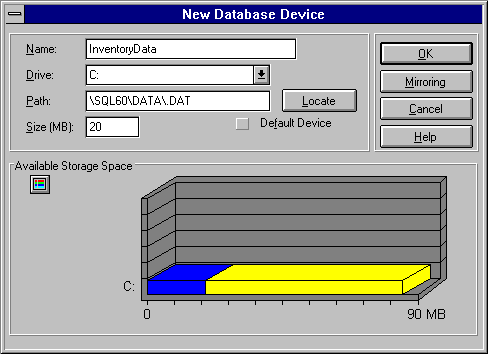
The Path box is filled in automatically using a combination of the name you entered in the Name box and the location of this SQL Server's MASTER device. To change the location, type a different path in the box, or choose the Locate button and select a different directory from the displayed directory tree.
Choose a size that is adequate for the intended use of this device. The Available Storage Space graph displays space available on the local drives. The size is represented in megabytes.
SQL Server mirroring is used to ensure full recovery and continued operation in the event of media failure. For more information on mirroring, see Chapter 7, Managing Drives.
The device is created.
When a database device is created, its logical and physical names are entered in the sysdevices table in the master database.
You can also create a new database device while creating or modifying a database. This allows you to create a new device at the time you create the database or transaction log the new device will support. For more information, see Chapter 6, Managing Databases.