 To mirror a device
To mirror a deviceMirroring can be set up using SQL Enterprise Manager or the DISK MIRROR statement. This chapter primarily describes the use of SQL Enterprise Manager. For information about using DISK MIRROR and other statements, see the Microsoft SQL Server Transact-SQL Reference.
When you mirror a device, SQL Enterprise Manager creates a new physical device (the mirror device) and puts an exact copy of the existing device (the mirrored device) on it. If the mirrored device has a lot of information on it, it might take a few minutes when you first mirror it. You should place the mirror device on a separate disk. Use SQL Enterprise Manager to mirror a device while creating a new device or editing an existing device.
 To mirror a device
To mirror a device
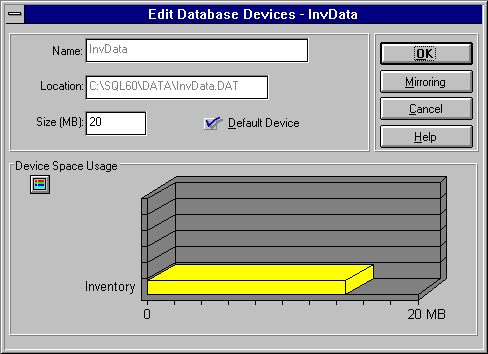
For more information on creating or modifying devices, see Chapter 5, Managing Devices.
The Database Device Mirroring dialog box appears.
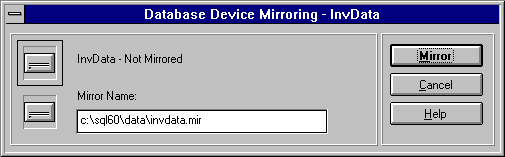
By default, the Mirror Name box is filled with the path to the MASTER.DAT file, followed by the first eight characters of the selected device's name plus the .MIR file extension. To place the mirror device on a separate drive, type a new path in the mirror name. For example: D:\MIRDIR\INVDATA.MIR.
All directories in the path must already exist. SQL Enterprise Manager will not create them.
The device is mirrored.