 To generate a SQL script
To generate a SQL scriptSQL Scripts are descriptions of the statements that are used to create database objects. With SQL Enterprise Manager, you can generate scripts from objects in an existing database. You can then add these objects to a database by running the scripts against that database. In effect, this copies and re-creates database objects. Another reason to generate scripts is to create a record of how a database was created.
You can generate a script for an entire database or for selected objects of that database.
 To generate a SQL script
To generate a SQL scriptThe Generate SQL Scripts dialog box appears.
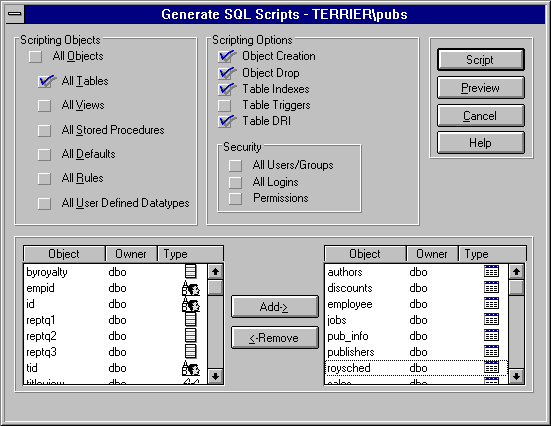
All objects in the database are added to the right-hand box at the bottom of the Generate SQL Scripts dialog box. Optionally, to exclude selected objects, select the objects, and choose Remove.
For example, to generate a script for all tables in the database, choose the All Tables option.
The objects are added to the right-hand box at the bottom of the Generate SQL Scripts dialog box. Optionally, to exclude selected objects, select the objects and choose Remove.
The object moves to the right-hand box. If you make a mistake, select the object from the right-hand box, and then choose Remove.
Select the options for the user information to be generated with the script. You can generate statements that add all users and groups to the database, that add all logins to SQL Server of the users associated with that database, and/or that add the permissions for the database.
The Object Scripting Preview dialog box appears.
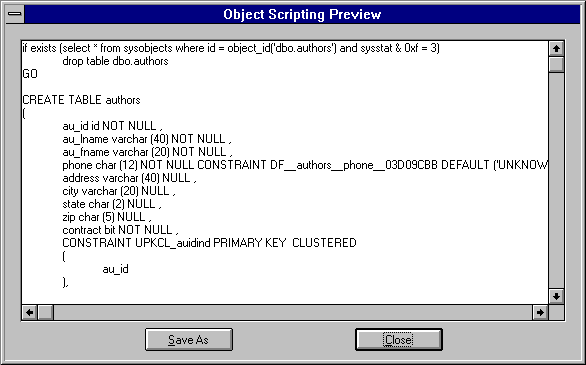
To modify the script, edit the text in the Object Scripting Preview box, choose the Save As button, and complete the Save As dialog box that appears.
The Save As dialog box appears.
Note When a script is run, it creates the database object(s), but it does not include data to a table that it creates. Data can be added, using the INSERT statement or can be copied in from the original table by using bcp or SQL Transfer Manager. When running a script in a non-empty database, the script might not be able to drop and/or create some items correctly (for example, user-defined datatypes) if those items are being used by other database objects.