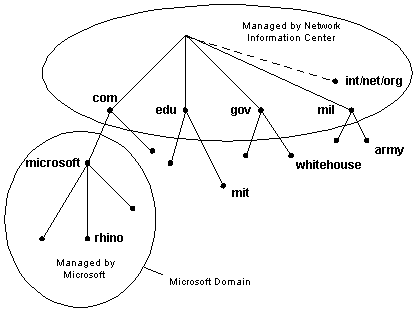
A Domain Name System is composed of a distributed database of names. The names in the DNS database establish a logical tree structure called the domain name space. Each node or domain in the domain name space is named and can contain subdomains. Domains and subdomains are grouped into zones to allow for distributed administration of the name space (zones will be discussed later in this section). The domain name identifies the domain's position in the logical DNS hierarchy in relation to its parent domain by separating each branch of the tree with a period ".". The following figure shows a few of the top level domains, where the Microsoft domain fits, and a host called "rhino" within the "microsoft.com" domain. If someone wanted to contact that host, they would use the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) rhino.microsoft.com.
