It is very important that you understand the difference between a zone and a domain. A zone is a physical file composed of resource records that defines a group of domains. A domain is a node in the DNS namespace and all subdomains below it.
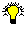
A zone is some portion of the DNS namespace whose database records exist and are managed in a particular zone file. A single DNS server might be configured to manage one or multiple zone files. Each zone is anchored at a specific domain node—referred to as the zone's "root domain." Zone files do not necessarily contain the complete tree (that is all subdomains) under the zone's root domain. For a comparison of domains and zones, look at the figure that follows. In this example, microsoft.com is a domain but the entire domain is not controlled by one zone file. Part of the domain is actually broken off into a separate zone file for dev.microsoft.com. Breaking up domains across multiple zone files might be needed for distributing management of the domain to different groups or possibly for efficiencies in data replication (that is zone transfers which will be discussed later).
|
|
It is very important that you understand the difference between a zone and a domain. A zone is a physical file composed of resource records that defines a group of domains. A domain is a node in the DNS namespace and all subdomains below it. |
