Name Resolution
Windows NT TCP/IP 3.5x systems may use several methods for locating NetBIOS resources:
- NetBIOS name cache
- NetBIOS name server
- IP subnet broadcasts
- Static LMHOSTS files
- Static HOSTS files
- DNS servers
Earlier implementations used only cache, broadcasts, and LMHOSTS files; however, in version 3.5, a NetBIOS name server (WINS) was added, and modifications were made to allow NetBIOS applications to query the DNS name-space by appending configurable domain suffixes to a NetBIOS name. However, the DNS name resolution was always done last after the NetBIOS cache, LMHOSTS file (if enabled), WINS (if enabled), and broadcast were tried. With Windows NT 4.0 the DNS name resolution will be tried first if the name is greater than 15 characters (maximum length of a NetBIOS computer name on Windows NT). The Host name can now be used in any of the
Windows NT utilities (such as Microsoft Explorer seen below) that previously supported NetBIOS computer names. This functionality will also be made available in the Windows® 95 operating system in the future.
|
 |
Remember that the \%SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\HOSTS file can still be used for Host name resolution. However, DNS will be queried before the HOSTS file is parsed.
If the DNS Host name (larger than 16 characters) is passed to a utility and there are 2 transports loaded on a workstation (TCP and NetBEUI), only the TCP transport will try to setup the session. If the Host name is not used and the NetBIOS name is used then all transports will be tried. |

In this example I could have also used:
\\157.55.100.204\public instead of \\scottsu-7.scottsu.com\public.
For more information on NetBIOS name resolution you can refer to the White Paper titled, "Microsoft Windows NT Server 3.5—NT203 Administration Tools of Windows NT Advanced ServerDynamic Host Configuration Protocol and Windows Internet Naming Service," part number 098-56544.
|
 |
On a Windows NT-based workstation, if a Host name is not found via DNS resolution, the name will be passed to NetBT (NetBIOS over TCPIP) for resolution via WINS, LMHOSTS file or broadcast. This might be seen as a feature for intranets that have many Web or FTP servers and want to get resolution via WINS for host queries.
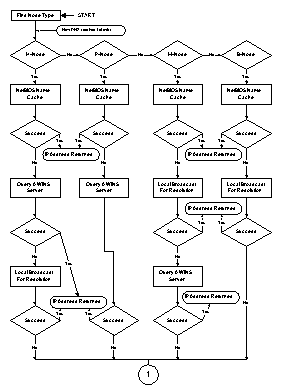
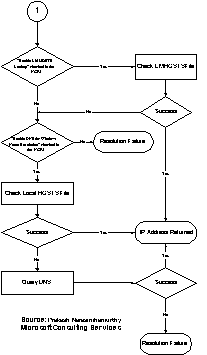
Prakash Narasimhamurthy of Microsoft Consulting Services provided the flow charts shown in the following figures to illustrate name resolution for the various node types. |
New
Windows NT Functionality