Objects can be classified as either container objects or noncontainer objects. Container objects (such as a directory) can logically contain other objects; noncontainer objects (such as a file) can't.
By default, when you create new objects within a container object, the new objects inherit permissions from the parent object. For example, in the following dialog box, D:\REPORTS\ANNM inherited permissions from its parent directory, D:\REPORTS.

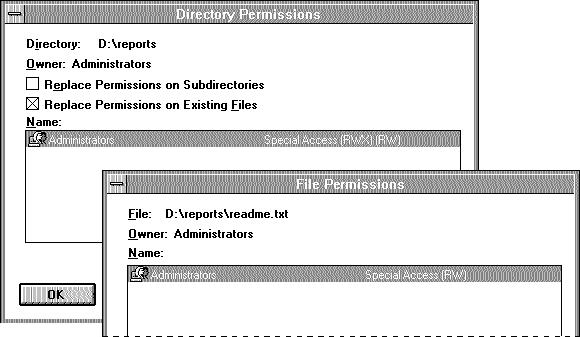
In the case of files and directories, when you change permissions on a directory, those changes affect that directory and its files but do not automatically apply to existing subdirectories and their contents. (They do, however, if you check the Replace Permissions On Existing Files check box.) You can apply the changed permissions to existing subdirectories and their files by selecting the Replace Permissions On Subdirectories check box.
The following dialog box shows the file permissions that are inherited from the parent directory by a file within that directory.