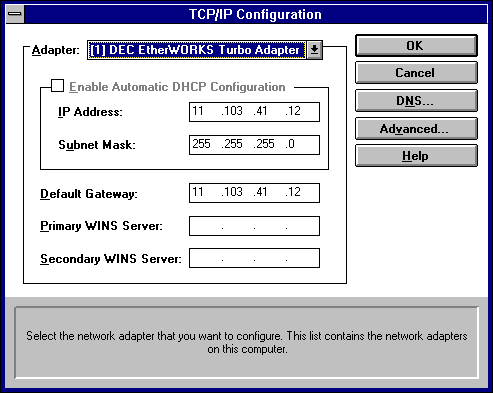
- In the Adapter box, select the network adapter for which you want to set IP addresses.
After the Microsoft TCP/IP protocol software is installed on your computer, you must manually provide valid addressing information if you are installing TCP/IP on a DHCP server or a WINS Server, or if you cannot use automatic DHCP configuration.
For a WINS server computer that has more than one network adapter card, WINS always binds to the first adapter in the list of adapters bound by TCP/IP. Make sure that this adapter address is not set to 0, and that the binding order of IP addresses is not disturbed.
You must be logged on as a member of the Administrators group for the local computer to configure TCP/IP.
Caution Be sure to use the values for IP addresses and subnet masks that are supplied by your network administrator to avoid duplicate addresses. If duplicate addresses do occur, this can cause some computers on the network to function unpredictably. For more information, see "IP Addressing" in Chapter 12, "Networking Concepts for TCP/IP."
If you are installing TCP/IP, perform the following steps.
– Or –
If you are reconfiguring TCP/IP, perform the following steps.

The Adapter list contains all network adapters to which IP is bound on this computer. This list includes all adapters installed on this computer.
You must set specific IP addressing information for each bound adapter with correct values provided by the network administrator. The bindings for a network adapter determine how network protocols and other layers of network software work together.
Table 11.2 Subnet Mask Defaults
Address class | Range of first octet in IP address | Subnet mask |
Class A | 1–126 | 255.0.0.0 |
Class B | 128–191 | 255.255.0.0 |
Class C | 192–223 | 255.255.255.0 |
This value specifies the IP address of the default gateway (or IP router) used to forward packets to other networks or subnets. This value should be the IP address of your local gateway.
This parameter is required only for systems on internetworks. If this parameter is not provided, IP functionality is limited to the local subnet unless a route is specified with the TCP/IP route utility, as described in Appendix A, "TCP/IP Utilities Reference."
If your computer has multiple network cards, additional default gateways can be added using the Advanced Microsoft TCP/IP Configuration dialog box, as described later in this chapter.
The network administrator should provide the correct values for these parameters. These are global values for the computer, not just individual adapters.
If an address for a WINS server is not specified, this computer uses name query broadcasts (the b-node mode for NetBIOS over TCP/IP) plus the local LMHOSTS file to resolve computer names to IP addresses. Broadcast resolution is limited to the local network.
Note
WINS name resolution is enabled and configured automatically for a computer that is configured with DHCP.
On a WINS server, NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NETBT.SYS) uses WINS on the local computer as the primary name server, regardless of how name resolution might be configured. Also, NetBIOS over TCP/IP binds to the first IP address on a network adapter and ignores any additional addresses.
For overview information about name resolution options, see "Name Resolution for Windows Networking" in Chapter 12 "Networking Concepts for TCP/IP." For detailed information about installing and configuring WINS servers, see Chapter 14, "Installing and Configuring WINS Servers."
Microsoft TCP/IP has been configured. If you are installing TCP/IP for the first time, you must restart the computer for the configuration to take effect. If you are changing your existing configuration, you do not have to restart your computer.
After TCP/IP is installed, the \systemroot\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\ETC directory contains a default HOSTS file and a sample LMHOSTS.SAM file. The network administrator might require that replacement HOSTS and LMHOSTS files be used instead of these default files.