If your computer has multiple network adapters connected to different networks using TCP/IP, you can choose the Advanced button in the TCP/IP Configuration dialog box to configure options for the adapters or to configure alternate default gateways.

The IP address and default gateway settings in this dialog box are defined only for the selected network adapter.
The network administrator should provide the correct values for this parameter.
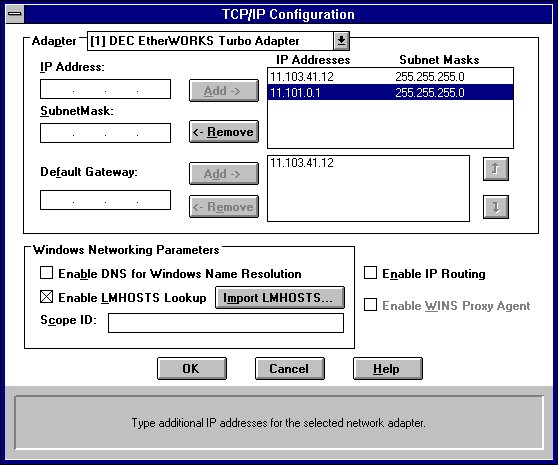
Optionally, if your network card uses multiple IP addresses, repeat this process for each additional IP address. You can specify up to five additional IP addresses and subnet masks for identifying the selected network adapter. This can be useful for a computer connected to one physical network that contains multiple logical IP networks.
Repeat this process for each additional gateway. The network administrator should provide the correct values for this parameter.
This list specifies up to five additional default gateways for the selected network adapter.
To change the priority order for the gateways, select an address to move and use the up- or down-arrow buttons. To remove a gateway, select it, and then choose the Remove button.
If this option is selected, the system finds the DNS server by using the IP address specified in the DNS Configuration dialog box, as described earlier in this chapter. Selecting this option enables DNS name resolution for use by Windows networking applications.
If you already have a configured LMHOSTS file, choose the Import LMHOSTS button and specify the directory path for the LMHOSTS file you want to use. By default, Windows NT uses the LMHOSTS file found in \systemroot\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\ETC.
For any method of name resolution used in a Windows NT network, the LMHOSTS file is consulted last after querying WINS or using broadcasts, but before DNS is consulted.
To communicate with each other, all computers on a TCP/IP internetwork must have the same scope ID. Usually, this value is left blank. A scope ID might be assigned to a group of computers that will communicate only with each other and no other systems. Such computers can find each other if their scope IDs are identical. Scope IDs are used only for communication based on NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
A computer can have only one scope ID, even if it has more than one adapter card with access to more than one network. If such a multihomed computer is a DHCP client, with DHCP servers on each network, the scope ID of the two networks should be identical. If they are not identical, the last adapter card to be configured will write its scope ID to the Registry, which could result in unexpected behavior and a loss of connectivity to one of the networks. It is best in this case to set the scope ID manually. Any manually configured value overrides values provided by the DHCP server.
The network administrator should provide the correct value, if required.
This option allows this computer to participate with other static routers on a network. You should check this option if you have two or more network cards and your network uses static routing, which also requires the addition of static routing tables. For information about creating static routing tables, see the route utility in Appendix A, "TCP/IP Utilities Reference."
This option is not available if your computer has only one network adapter and one IP address. Also, this option does not support routers running the Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
This option allows the computer to answer name queries for remote computers, so other computers configured for broadcast name resolution can benefit from the name resolution services provided by a WINS server.
This option is available only if you entered a value for a primary WINS server in the TCP/IP Configuration dialog box, as described in "Configuring TCP/IP" earlier in this chapter. However, the proxy agent cannot be run on a computer that is also a WINS server.
Consult with the network administrator to determine whether your computer should be configured as a WINS proxy agent, as only a few computers on each subnetwork should be configured for this feature.
You must restart the computer for the changes to take effect.