Windows NT version 3.5 RAS was not designed to route packets from a local area network over a WAN link. However, by correctly configuring both the RAS computer acting as a router and the other computers on your small LAN, you can use the computer running Windows NT RAS as a simple router to the Internet.
The following items are the primary requirements to use Windows NT RAS as router between your LAN and the Internet.
Note The Internet service provider you connect to cannot be a Windows NT 3.5 computer.
To be identified using names rather than IP addresses, you also need a domain name. Your Internet service provider might help you obtain a domain name.
When you establish your PPP account, you must also ensure your Internet service provider provides you with a valid class C network (255 nodes) or a valid IP subnet (and subnet mask) that contains sufficient IP addresses for every computer on your LAN.
Once you have a PPP connection, IP addresses for your subnet (and correct subnet mask), and (optionally) a domain name, you can then configure the RAS and LAN computers for Internet gateway as described below.
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasArp\Parameters
DisableOtherSrcPackets REG_DWORD
By default, the header of each packet sent by the RAS computer over the PPP link uses the IP address of the RAS computer as the source. Since the packets that come from LAN clients are not originating from the RAS computer, you must set DisableOtherSrcPacket to 1 so the header sent over the PPP link retains the IP address of the LAN clients.
Range: 0-1
Default: 0 (not in registry)
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\PPP\IPCP
PriorityBasedOnSubNetwork REG_DWORD
A computer can connect to the LAN using a network card and a RAS connection. If the RAS connection and the LAN network adapter card are assigned addresses with the same network number and the Use Default Gateway On Remote Network check box is selected, then all packets are sent over the RAS connection, though the two addresses are in different subnetworks within the same network.
Set this parameter to 1 to send packets over the network card. For example, if the network adapter card has IP address 10.1.1.1 (subnet mask 255.255.0.0) and the RAS connection is assigned the address 10.2.1.1, RAS sends all 10.x.x.x packets using the RAS connection. If the parameter is set, RAS sends 10.2.x.x packets using the RAS connection and 10.1.x.x packets using the network adapter card.
Range: 0-1
Default: 0 (not in registry)
The default gateway is set when you configure the TCP/IP protocol.
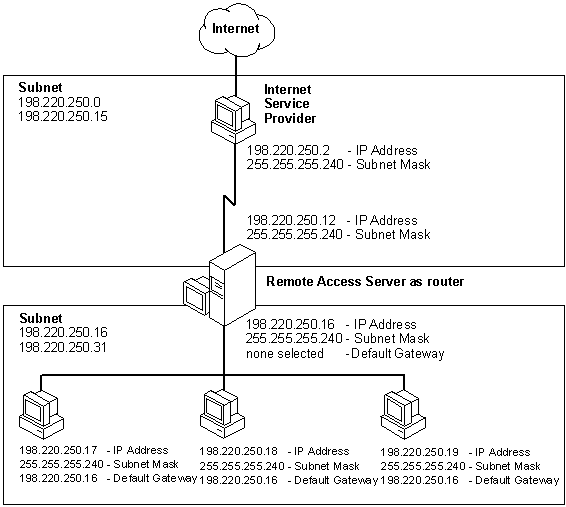
Use the IP address of the network card adapter in the RAS computer as the default gateway for all computers on the LAN except the computer acting as a router to the Internet. The default gateway for the computer acting as the router to the Internet should be left blank. Consult the following figure to determine the correct assignment pattern of IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways.

Figure 22.5 Sample Configuration using RAS as a Simple Internet Router