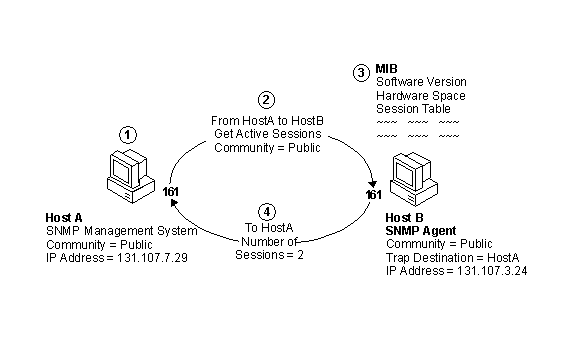
This section describes, at a high level, the processing that occurs when a management system sends a request to a Windows NT SNMP agent.

The numbers here correspond to the numbers in the preceding figure.
1. The network management system initiates a request to SNMP agent Host A. The SNMP packet contains the following information:
2. The request is passed by the application to socket 161, where the host name is resolved to an IP or IPX address. The packet is routed to socket 161 on the agent.
3. The SNMP agent receives and processes the request.
The community name is verified. If the community name is invalid or the packet is ill-formed, the SNMP agent discards the request.
If the community name is valid, the agent verifies the source host name, IP address, or IPX address. The agent must be authorized to accept packets from the management system, or it discards the packet.
The SNMP agent passes the request to the appropriate DLL, which retrieves the information from the associated MIB. The table in the preceding section, "Windows NT Files Installed for SNMP," identifies the DLLs.
The DLL returns the information to the SNMP agent.
4. The SNMP agent builds the "response" packet with the requested information and sends it to the SNMP manager.
Note
Port 161 is used for SNMP messages and port 162 is used for SNMP traps.