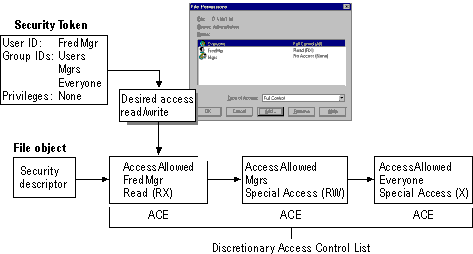
A user whose user ID is FredMgr tries to open and change a file G:\File1.txt. The file has the discretionary ACL as shown in the next figure. The FredMgr access token indicates that he is a member of the groups Users, Mgrs, and Everyone.
Note
The order in which permissions are listed by the File Permissions dialog box doesn't necessarily reflect the order in which ACEs are processed by Windows NT. It is important to note, however, that the Permissions Editor (controlled by means of this dialog box) orders all AccessDenied ACEs first so that they are the first to be processed within each ACL.

In this example, Windows NT evaluates the ACL by comparing the desired access mask with each ACE and processes the desired mask as follows:
1. Windows NT reads FredMgr's desired access mask to see that he is trying to gain Read and Write access.
2. Windows NT reads the AccessAllowed ACE for FredMgr and finds a match to the Read permission requested in the desired access mask.
3. Windows NT reads the AccessAllowed ACE for Mgrs and finds a match to the Write permission requested in desired access mask.
At this point, processing of the ACL stops even though there is another ACE in the ACL. Processing stops, and access is granted because Windows NT found matches for everything in the desired access mask.