
All user-mode requests go through the Workstation service. This service consists of two components.
The Workstation service receives the user request, and passes it to the kernel-mode redirector.

Figure 1.20 Workstation Service
The redirector (RDR) is a component that resides above TDI and through which one computer gains access to another computer. The Windows NT operating system redirector allows connection to Windows for Workgroups, LAN Manager, LAN Server, and other MS-Net-based servers. The redirector communicates to the protocols by means of the TDI interface.
The redirector is implemented as a Windows NT file system driver. Implementing a redirector as a file system has several benefits, which are listed below.
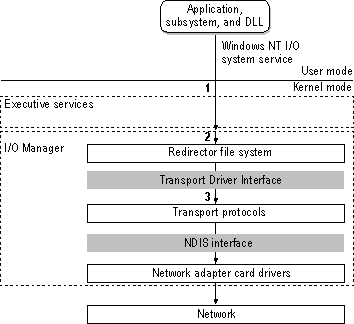
Figure 1.21 Windows NT redirector
Besides allowing connections to LAN Manager, LAN Server, and MS-Net servers, the Windows NT redirector can coexist with redirectors for other networks, such as Novell NetWare and Banyan VINES.
While Windows NT includes integrated networking, its open design provides transparent access to other networks. For example, a computer running Windows NT Server can concurrently access files stored on Windows NT and NetWare servers.
For each additional type of network, such as NetWare or VINES, you must install a component called a provider. The provider is the component that allows a computer running Windows NT Server or Windows NT Workstation to communicate with the network. The Windows NT operating system includes two providers; Client Services for NetWare and Gateway Services for NetWare.
Client Services for NetWare is included with Windows NT Workstation and allows a computer running Windows NT Workstation to connect as a client to the NetWare network. The Gateway service, included with Windows NT Server, allows a computer running Windows NT Server to connect as a client to the NetWare network. Other provider DLLs are supplied by the appropriate network vendors.
When a process on a Windows NT computer tries to open a file that resides on a remote computer, the following steps occur.
First, the process calls the I/O Manager to request that the file be opened.
Then, the I/O Manager recognizes that the request is for a file on a remote computer, and passes the request to the redirector file-system driver.
Finally, the redirector passes the request to lower-level network drivers, which transmit it to the remote server for processing.
Configuration requirements for loading the Workstation service include: