The scenario described in this section was an actual pilot test of Windows NT as an Internet gateway server at Microsoft Corporation. For security reasons, the Internet gateway server was installed on an isolated network, which was in turn connected to the Internet by third-party routers. The RAS server and the third-party routers were not connected to the corporate network.

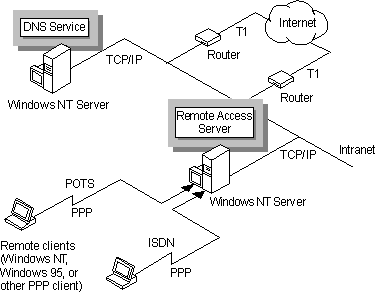
Figure 6.4 Windows NT as an Internet gateway server
In this scenario, the computer running Windows NT Server has a leased line to an Internet service provider through third-party routers. The Remote Access Service is installed. This enables traffic from the Internet to be routed to and from computers on the private network. The Remote Access Service enables Windows Dial-Up Networking clients or other dial-up clients to connect to the RAS server by using ISDN or a POTS line (plain old telephone service, also known as PSTN or public switched telephone network), giving them Internet access.
The Internet gateway server for the pilot test had the following configuration:
For more information about the Remote Access Service, see the Windows NT Server Networking Supplement and Windows NT Server Resource Kit Networking Guide.