This chapter describes the workspace BIFF file, which is the file that Microsoft Excel writes when you choose the Save Workspace command from the File menu. The workspace file stores the position, size, filename, window attributes, and so on, of each workbook window.
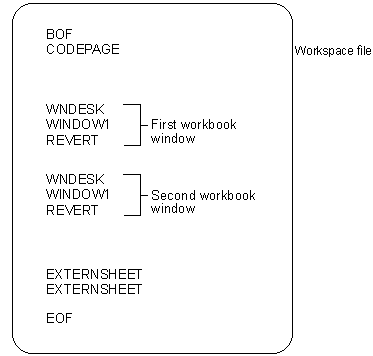
The following illustration shows the workspace file for a workspace with two workbook windows. The file contains global BOF, CODEPAGE, and EOF records. There is a set of WNDESK, WINDOW1, and REVERT records for each window, and at the end of the file, an EXTERNSHEET record for each window.

The workspace BIFF file is not an OLE 2 compound file, therefore you must use the Dumpbiff.exe utility (an MS-DOS program) to examine the file. For general information about BIFF records, see BIFF Record Information.
The first two fields in every BIFF record are record number and record length. Because these fields have the same offset and size in every BIFF record, they are not documented in the following descriptions.
The BOF record marks the beginning of the file.
BOF Record Number Field
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
0 |
vers |
1 |
ver: |
|
1 |
bof |
1 |
09h |
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
vers |
2 |
Version number (0500 for BIFF5 and BIFF7) |
|
6 |
dt |
2 |
Substream type: |
|
8 |
rupBuild |
2 |
Build identifier (internal use only) |
|
10 |
rupYear |
2 |
Build year (internal use only) |
The rupBuild and rupYear fields contain numbers that identify the version (build) of Microsoft Excel that wrote the file. If you write a BIFF file, you can use the BiffView utility to determine the current values of these fields by examining any BOF record in a workbook file.
The CODEPAGE record stores the default code page (character set) that was in use when the workspace was saved.
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
cv |
2 |
Code page the file is saved in: |
The EOF record marks the end of the file. It has no record data field, and is simply 0A000000h.
The EXTERNSHEET record specifies an externally referenced workbook in the workspace. You should not change the order of EXTERNSHEET records.
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
cch |
1 |
Length of filename |
|
5 |
rgch |
var |
Filename |
The cch field contains the length of the source workbook filename. The rgch field contains the source workbook filename.
Whenever possible, filenames are encoded to make BIFF files transportable across file systems. Encoded filenames are identified by the first character of the rgch field. The first character of the rgch field may be any one of the following values.
|
Name |
Value |
Meaning |
|
chEmpty |
00 |
Reference to an empty workbook name (see text) |
|
chEncode |
01 |
Filename has been encoded (see following table) |
|
chSelf |
02 |
Self-referential external reference (see text) |
chEmpty indicates that the filename is an external reference to an empty workbook name, as in the formula =Sheet1!$A$1.
chSelf indicates that the filename is an external reference where the dependent and source workbooks are the same. An example of this is a workbook SALES.XLS that contains the formula =SALES.XLS!$A$1.
A chEncode at the beginning of rgch indicates that the filename of the source workbook has been encoded to a less system-dependent filename. The following special keys are recognized in the rgch field.
|
Name |
Value |
PC file systems |
Macintosh file system |
|
chVolume |
01 |
Represents an MS-DOS drive letter. It is followed |
Represents a single-character volume name. Because single-character volume names are uncommon on the Macintosh, the chLongVolume key is used to represent volume names that are longer than a single character. |
|
chSameVolume |
02 |
Indicates that the source workbook is on the same drive as the dependent workbook (the drive letter is omitted). For example, |
Indicates that the source workbook is on the same volume as the dependent workbook (the volume name is omitted). |
|
chDownDir |
03 |
Indicates that the source workbook is in a subdirectory of the current directory. For example, |
Indicates that the source workbook is in a folder in the current folder. For example, the formula =':XL:Sales1992'!A1 generates the chDownDir key. The folder name precedes the chDownDir key, and the filename follows it. |
|
chUpDir |
04 |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the parent directory of the current directory. For example, |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the parent folder of the current folder. For example, the formula ='::Sales1992'!A1 generates the chUpDir key. |
|
chLongVolume |
05 |
(not used) |
The chLongVolume key is followed by the length of the name (1 byte) and then by the volume name string. |
|
chStartupDir |
06 |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the startup directory (the XLSTART subdirectory of the directory that contains EXCEL.EXE). |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the Excel Startup Folder (5), which is in the System Folder. |
|
chAltStartupDir |
07 |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the alternate startup directory. |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the alternate startup folder. |
|
chLibDir |
08 |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the LIBRARY directory. |
Indicates that the source workbook is in the Macro Library folder. |
This record stores internal data for revert-to-saved processing.
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
rgch |
var |
Revert array; for internal use only |
The WINDOW1 record contains workbook-level window attributes. The xWn and yWn fields contain the location of the window in units of 1/20 of a point, relative to the upper-left corner of the Microsoft Excel window client area. The dxWn and dyWn fields contain the window size, also in units of 1/20 of a point.
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
xWn |
2 |
Horizontal position of the window |
|
6 |
yWn |
2 |
Vertical position of the window |
|
8 |
dxWn |
2 |
Width of the window |
|
10 |
dyWn |
2 |
Height of the window |
|
12 |
grbit |
2 |
Option flags |
|
14 |
itabCur |
2 |
Index of selected workbook tab (0-based) |
|
16 |
itabFirst |
2 |
Index of first displayed workbook tab (0-based) |
|
18 |
ctabSel |
2 |
Number of workbook tabs that are selected |
|
20 |
wTabRatio |
2 |
Ratio of width of the workbook tabs to the width of the horizontal scroll bar; to obtain the ratio, convert to decimal and then divide by 1000. |
The grbit field contains the following option flags.
|
Offset |
Bits |
Mask |
Name |
Contents |
|
0 |
0 |
01h |
fHidden |
= 1 if the window is hidden |
|
1 |
02h |
fIconic |
= 1 if the window is currently displayed as an icon | |
|
2 |
04h |
(reserved) | ||
|
3 |
08h |
fDspHScroll |
= 1 if horizontal scroll bar is displayed | |
|
4 |
10h |
fDspVScroll |
= 1 if vertical scroll bar is displayed | |
|
5 |
20h |
fBotAdornment |
= 1 if workbook tabs are displayed | |
|
7-6 |
C0h |
(reserved) | ||
|
1 |
7-0 |
FFh |
(reserved) |
The WNDESK record describes each window that appears in the workspace.
Record Data
|
Offset |
Name |
Size |
Contents |
|
4 |
ish |
2 |
Document number (zero-based) |
|
6 |
dt |
2 |
Document type; always = 0005h |