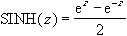
Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number.
Syntax
SINH(number)
Number is any real number.
The formula for the hyperbolic sine is:
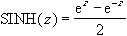
Examples
SINH(1) equals 1.175201194
SINH(-1) equals -1.175201194
You can use the hyperbolic sine function to approximate a cumulative probability distribution. Suppose a laboratory test value varies between 0 and 10 seconds. An empirical analysis of the collected history of experiments shows that the probability of obtaining a result, x, of less than t seconds is approximated by the following equation:
P(x<t) = 2.868 * SINH(0.0342 * t), where 0<t<10
To calculate the probability of obtaining a result of less than 1.03 seconds, substitute 1.03 for t:
2.868*SINH(0.0342*1.03) equals 0.101049063
You can expect this result to occur about 101 times for every 1000 experiments.