A row has a state that depends on whether it has been changed and whether that change is pending or transmitted. Consumers call IRowsetUpdate::GetRowStatus to determine the state of a row. They call IRowsetUpdate::GetPendingRows to get all rows in a pending change state. The state is indicated by the DBPENDINGSTATUS enumerated type. The values in this type have the following meanings.
| Value | State name | Description |
| DBPENDINGSTATUS_ NEW |
Pending Insert | The row has a pending insert. |
| DBPENDINGSTATUS_ CHANGED |
Pending Update | The row has a pending update. |
| DBPENDINGSTATUS_ DELETED |
Pending Delete | The row has a pending delete. |
| DBPENDINGSTATUS_ UNCHANGED |
Unchanged | No changes have been made to the row, or changes have been made to the row and have been transmitted or undone. |
| DBPENDINGSTATUS_ INVALIDROW |
Deleted | The row has been deleted and that deletion has been transmitted to the data source. This status is also used when a row handle passed to GetRowStatus was invalid. |
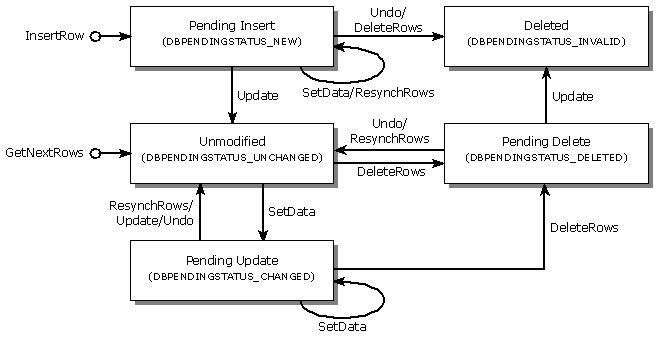
The Unchanged and Deleted states are the nonending change states. The Pending Update, Pending Delete, and Pending Insert states are the pending change states. The following figure shows these states, how methods affect them, and the corresponding DBPENDINGSTATUS values.
Pending change states

If the consumer calls IRowset::ReleaseRows for a row and the reference count for that row falls to zero, release of the row and its resources depends on the row's state. In the nonpending change states, the row and its resources are usually released when the reference count falls to zero, although the actual point of release is provider specific.
In the pending change states, the row and its resources are not released when the reference count falls to zero, nor are the pending changes lost. The row remains valid until the changes are transmitted or undone (the row moves to a nonpending change state), then the row and its resources are released. Rows in a pending change state that have a reference count of zero are still considered active for purposes such as calculating row limits such as those returned by the DBPROP_MAXOPENROWS and DBPROP_MAXPENDINGROWS properties. Although the row handle might remain valid for such rows, consumers should not count on this.