Bit | Definition |
0 | Exists |
1 | ATDFields |
3-2 | StructType |
4 | FNULLBits |
5 | 0 SecondaryPtr valid |
6 | 0 SiblingPtr valid |
7 | Reserved |
15-8 | CompressionID |

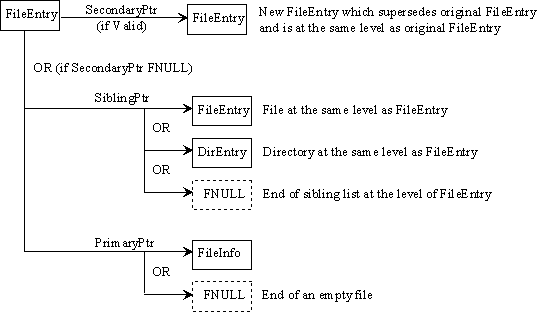
Figure 4
Figure 4 depicts how each pointer type within a FileEntry is related to all valid subsequent structures.