Message | Outgoing Call | Incoming Call |
Call Request | NTS>Dial Request | FEP>Call is Ringing |
Call Reply | FEP>Call Has Connected, FEP knows connect speed, FEP sends window and time-out. | NTS>FEP told to answer call. |
Call Connected | N/A | FEP>FEP indicates that call has been answered and speed negotiated. FEP sends window and time-out. |
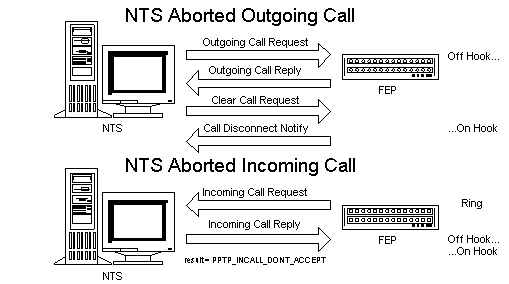
Figure 2. How calls can be aborted by the NTS
Figure 3 illustrates how the FEP would abort/disconnect calls.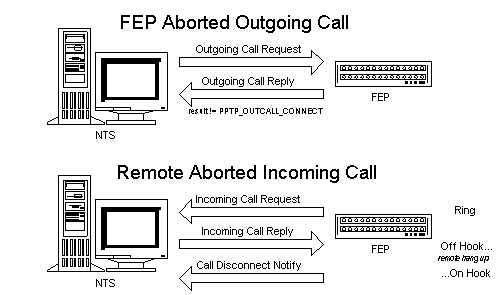
Figure 3. How FEP aborts/disconnects calls
Back to table of contents.The Outgoing Call Request is sent by the NTS when it needs to place an outgoing call. The NTS can request packet framing and call bearer capabilities as follows:
/*
* Packet framing type:
*
* PPTP_ASYNC_FRAMING: Async PPP.
*
* PPTP_SYNC_FRAMING: Sync PPP.
*/
typedef enum {
PPTP_ASYNC_FRAMING = 1,
PPTP_SYNC_FRAMING,
PPTP_DONT_CARE_FRAMING
} PptpFramingType;
/*
* Call bearer type.
*
* PPTP_ANALOG_CALL: This is an analog call.
*
* PPTP_DIGITAL_CALL: This is a digital call.
*
* PPTP_DONT_CARE_BEARER_TYPE: Don't care what you use.
*/
typedef enum {
PPTP_ANALOG_CALL = 1,
PPTP_DIGITAL_CALL,
PPTP_DONT_CARE_BEARER_TYPE
} PptpCallBearerType;The packet format for the Outgoing Call Request is the following:
/*
* The CallRequest Packet.
*
* This command can be sent from the NT to the FEP to
* indicate a request for an outgoing call.
*
* callID: A unique identifier assigned by
* the transmitter of this message.
* This field can be used for routing
* purposes.
*
* callSerialNumber A unique identifier assigned by
* the transmitter of this message.
* This field can be used to log events
* associated with the call.
*
* minBPS: The lowest acceptable BPS for
* outgoing calls.
*
* maxBPS: The highest acceptable BPS for
* outgoing calls.
*
* bearerType: Call bearer type. One of
* PptpCallBearerType.
*
* framingType: Link framing type. One of
* PptpFramingType.
*
* packetWindow: The receive packet window of
* the *sender* of this message.
*
* packetProcDelay: The packet processing delay
* time for the sender of this packet.
* This value is in 10ths of a second.
* For example, 64 would mean 6.4
* seconds.
*
* phoneNumberLength: The actual number of valid digits
* in the phoneNumber field.
*
* phoneNumber: The number that is to be dialed.
* For ISDN and analog calls, the
* phone number must be in ASCII.
*
* subAddress: Sub-address field.
*
*/
typedef struct {
Word callID;
Word callSerialNumber;
LongWord minBPS;
LongWord maxBPS;
LongWord bearerType;
LongWord framingType;
Word packetWindow;
Word packetProcDelay;
Word reserved;
Word phoneNumberLength;
Word reserved;
Byte phoneNumber[ 64 ];
Byte subAddress[ 64 ];
} PptpOutCallRequest;The result of the call is returned in this packet and can have one of the following values:
/*
* Result Codes for Call Replies.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_CONNECT: Call connected successfully.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_GENERAL_ERROR: See the generalErrorCode field.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_NO_CARRIER: No carrier.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_BUSY: Got a busy signal.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_NO_DIAL_TONE: No dial tone.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_TIMEOUT: The call did not complete in time.
*
* PPTP_OUTCALL_DONT_ACCEPT: Do not accept this call.
*/
typedef enum {
PPTP_OUTCALL_CONNECT = 1,
PPTP_OUTCALL_GENERAL_ERROR = 2,
PPTP_OUTCALL_NO_CARRIER,
PPTP_OUTCALL_BUSY,
PPTP_OUTCALL_NO_DIAL_TONE,
PPTP_OUTCALL_TIMEOUT,
PPTP_OUTCALL_DONT_ACCEPT
} PptpCallResultCode;The packet format is the following:
/*
* The CallReply packet.
*
* callID: A unique identifier assigned by
* FEP. This field can be used
* for routing purposes.
*
* peersCallID: Set to the value received in the
* Outgoing Call Request Message.
*
* resultCode: One of PptpCallResultCode.
*
* generalErrorCode: Contains the general error if
* resultCode is *_GENERAL_ERROR.
*
* causeCode: This is the cause code and can
* vary from call type to call type.
* For ISDN calls, it is the Q.931
* cause code.
*
* connectSpeed: The actual connected speed in BPS.
*
* packetWindow: The receive packet window of
* the *sender* of this message.
*
* packetProcDelay: The packet processing delay
* time for the sender of this packet.
* This value is in 10ths of a second.
* For example, 64 would mean 6.4
* seconds.
*
* physChannelID: This field is initialized by
* FEP, in a vendor-specific manner,
* which defines which physical channel
* number was used for this outgoing
* call.
*/
typedef struct {
Word callID;
Word peersCallID;
Byte resultCode;
Byte generalErrorCode;
Word causeCode;
LongWord connectSpeed;
Word packetWindow;
Word packetProcDelay;
LongWord physChannelID;
} PptpOutCallReply;The Incoming Call Request is sent by the FEP to the NTS when a client calls the FEP. The format of this message is the following:
/*
* The Incoming Call Request packet. Sent by the FEP to the
* NTS.
*
* callID: A unique identifier assigned by
* the FEP. This field can be used
* for routing purposes.
*
* callSerialNumber A unique identifier assigned by
* the FEP. This field can be used
* to log events associated with
* the call.
*
* callBearerType: One of PptpCallBearerType.
*
* physChannelID: This field is initialized by
* FEP, in a vendor-specific manner,
* which defines which physical channel
* number was used for this incoming
* call.
*
* dialedNumberLength: The actual number of valid digits
* in the dialedNumber field.
*
* dialingNumberLength: The actual number of valid digits
* in the dialingNumber field.
*
* dialedNumber: The number that was dialed by the
* caller.
*
* dialingNumber: The phone number of the client.
*
* subAddress: The sub-address number.
*
*/
typedef struct
Word callID;
Word callSerialNumber;
LongWord callBearerType;
LongWord physChannelID;
Word dialedNumberLength;
Word dialingNumberLength;
Byte dialedNumber[ 64 ];
Byte dialingNumber[ 64 ];
Byte subAddress[ 64 ];
} PptpInCallRequest;This message is sent by the NTS to the FEP as a reply to the Incoming Call Request sent by the FEP. The resultCode field in the Incoming Call Reply message can be one of the following:
/*
* Possible result code sent by the NTS to the FEP in the
* Incoming Call Reply.
*
* PPTP_INCALL_ACCEPT: Go ahead and answer the call.
*
* PPTP_INCALL_GENERAL_ERROR: See the generalErrorCode field.
*
* PPTP_INCALL_DONT_ACCEPT: Don't accept the call. Hang up.
*
*/
typedef enum {
PPTP_INCALL_ACCEPT = 1,
PPTP_INCALL_GENERAL_ERROR = 2,
PPTP_INCALL_DONT_ACCEPT,
} PptpInCallResultCode;
/*
* The Incoming Call Reply packet.
*
* callID: A unique identifier assigned by
* the NTS. This field can be used
* for routing purposes.
*
* peersCallID: Set to the value received in the
* callID field in the Incoming Call
* Request.
*
* resultCode: One of PptpCallResultCode.
*
* generalErrorCode: Contains the general error code if
* resultCode is *_GENERAL_ERROR.
*
* packetWindow: The receive packet window of
* the *sender* of this message.
*
* packetProcDelay: The packet processing delay
* time for the sender of this message.
* This value is in 10ths of a second.
* For example, 64 would mean 6.4
* seconds.
*/
typedef struct
Word callID;
Word peersCallID;
Byte resultCode;
Byte generalErrorCode;
Word packetWindow;
Word packetProcDelay;
Word reserved;
} PptpInCallRequest;The format of this command is the following:
/*
* The IncomingCallConnected packet.
*
* callID: Set to the value that was in the
* callID field in the Incoming Call
* Request message.
*
* peersCallID: Set to the value that was in the
* callID field in the Incoming Call
* Reply message.
*
* connectSpeed: Actual connected speed, in BPS.
*
* packetWindow: The receive packet window of
* the *sender* of this message.
*
* packetProcDelay: The packet processing delay
* time for the sender of this message.
* This value is in 10ths of a second.
* For example, 64 would mean 6.4
* seconds.
*
* framingType: The type of framing.
*
*/
typedef struct {
Word callID;
Word peersCallID;
LongWord connectSpeed;
Word packetWindow;
Word packetProcDelay
LongWord callFramingType;
} PptpInCallConnected;The format for this command is the following:
/*
* PptpCallClearRequest
*
* This message is sent by a server to request a disconnect of a
* connected call.
*
* callID: Call ID value used by originator.
* This field is used instead of the
* peer call ID because the value
* of the peer call ID may not
* be known during call establishment.
*
* reserved: Currently used for padding
*
*/
typedef struct {
Word callID;
Word reserved;
} PptpClearCallRequest;Possible reasons for the call being cleared can be the following:
/*
* Call Disconnect Notify Codes.
*
*/
typedef enum {
PPTP_DISCONNECT_LOST_CARRIER = 1,
PPTP_DISCONNECT_GENERAL_ERROR = 2,
PPTP_DISCONNECT_ADMIN_SHUTDOWN,
} PptpCallDisconnectCode;The format for this command is the following:
/*
* The CallDisconnectNotify message. There is no reply to this
* message.
*
* callID: Call ID value used by originator.
* This field is used instead of the
* peer call ID because the value
* of the peer call ID may not
* be known during call establishment.
*
* resultCode: One of CallDisconnectCode.
*
* generalErrorCode: A PptpGeneralErrorCode if resultCode is
* PPTP_DISCONNECT_GENERAL_ERROR.
*
* causeCode: This is the cause code and can
* vary from call type to call type.
* For ISDN calls, it is the Q.931
* cause code.
*
* callStatistics: Vendor-specific call statistics
* that can be logged for diagnostic
* purposes. Must be a null-terminated
* ASCII string.
*/
typedef struct {
Word callID;
Byte resultCode;
Byte generalErrorCode;
Word causeCode;
Word reserved;
Byte callStatistics[ 128 ];
} PptpCallDisconnectNotify;The format for this command is the following:
/*
* The WanErrorNotify message. There is no reply to this
* message.
*
* peersCallID: The peer's call identifier.
*/
typedef struct {
Word peersCallID;
Word reserved;
LongWord crcErrors;
LongWord framingErrors;
LongWord hardwareOverRuns;
LongWord bufferOverRuns;
LongWord timeoutErrors;
LongWord alignmentErrors;
} PptpWanErrorNotify;The message format is the following:
/*
* PptpSetLinkInfo
*
* This message is sent by the server to set the PPP LCP
* options processing that should be done by a client, so
* it can be offloaded from the server to obtain better
* PPP throughput.
*
* peerCallID Call ID value used by peer.
* This field is filled in with
* the callID field from the
* message sent by the peer
* during call establishment.
*
* reserved Currently used for padding.
*
* sendAccm Send ACCM value the client should use
* to process outgoing PPP packets.
* The default value used by the client until
* this message is received is 0XFFFFFFFF.
*
* recvAccm: Recv ACCM value the client should use
* to process incoming PPP packets.
* The default value
* used by the client until this
* message is received is 0XFFFFFFFF.
*/
typedef struct {
Word peerCallID;
Word reserved;
LongWord sendAccm;
LongWord recvAccm;
} PptpSetLinkInfo;