As discussed in Chapter 2, the thin-client/server architecture works with and enhances access to client/server and Web-based computing models. You can use the Internet, intranets, or extra-nets to deploy information and applications to groups that require different levels of security.
You can also combine a thin-client/server solution with Web architecture to provide some very intriguing possibilities. For example, you can extend the typical “download-and-run” Java paradigm of delivering application applets to a browser by adding a thin-client/server client to your browser with application activation from a Web page. To do this, you first create a Web page with an intuitive user interface that is customized specifically for your organization. You can then publish any type of application on your Web site—whether it’s an information application, a productivity application, or a mission-critical application.
Combine the Internet, intranets, and extranets with thin-client/server computing for a powerful solution.
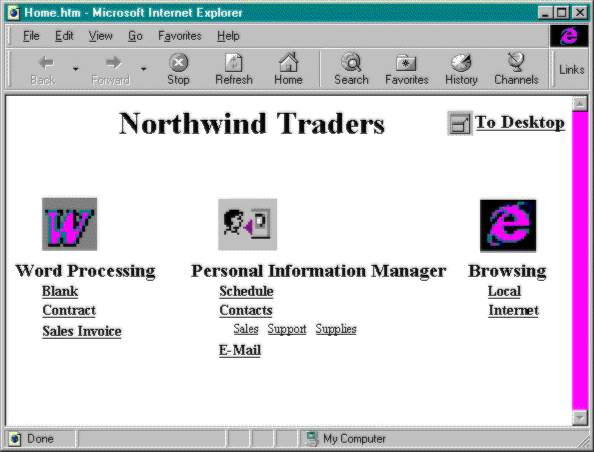
Users can run applications from customized Web pages instead of from their desktops. Or, to take this example further, a browser can automatically display your organization’s home page whenever a user starts his or her desktop computer, as shown in Figure 7-1.
FIGURE 7-1
Simple customized home page for deploying typical applications and information

Figure 7-1 shows the home page for an administrative assistant at the fictitious company Northwind Traders. Across the top of the page, application icons, paired with the most common templates for creating documents, appear for starting the most frequently used tasks and applications. Each user has a stored set of custom settings for creating a startup home page with a limited set of choices. Because the home page, the Web browser, and the appli-cations are stored and executed on the server, the IS department can easily maintain all of them.
As another option, you can have an Independent Computing Architecture (ICA)–enabled Web browser that resides on either a network computer or a personal computer, with the applications accessible from the HTML Web pages and executing on the ser-ver. The terms “launching” and “embedding” describe the ways that you can use HTML Web pages for starting applications. Launching simply refers to starting an application in a new window from a link on the Web page, as illustrated in Figure 7-2. Embedding takes that a step further: the application is executed and then runs in a defined space within a Web page, as illustrated in Figure 7-2.
You can embed an application in a Web page or run it from a separate window
FIGURE 7-2
Application launching and embedding from an HTML page
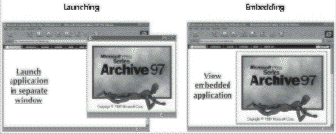
Application launching and embedding (ALE) allows your organization to customize its intranets and extranets by “publishing” any applications without having to adapt the application to some standardized, predetermined user interface. These embedded applications can then be accessed via the World Wide Web, as well as via the organization’s local area network (LAN) or intranet.
Web computing and thin-client/server technology combine to deliver all types of applications.
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to combine thin-client/server solutions and Web-based technology to create applications that are accessible over the Web. You’ll see how an organization can use HTML-based browsers to launch and embed applications with the WinFrame application server accessed by ICA for Web-based computing.
In Chapter 8, you’ll read some case studies about companies and organizations that are successfully using thin-client/server architecture. One company, Claimsnet.com, uses the World Wide Web for processing its subscribers’ health claims. Other companies are looking at expanding their thin-client/server solutions to work with Web servers that take advantage of HTML. Of particular interest is the combination of Web-based computing and thin-client/server solutions for educational institutions at which a lack of funds, use of old equipment, and a lack of IS support prohibit effective use of the latest technology.