Private Sub UserControl_Initialize()
Debug.Print "Initialize"
End Sub
Private Sub UserControl_InitProperties()
Debug.Print "InitProperties"
End Sub
Private Sub UserControl_ReadProperties(PropBag As _
PropertyBag)
Debug.Print "ReadProperties"
End Sub
Private Sub UserControl_WriteProperties(PropBag _
As PropertyBag)
Debug.Print "WriteProperties"
End Sub
Private Sub UserControl_Terminate()
Debug.Print "Terminate"
End Sub
Note For UserControl objects, Load and Unload are superseded by the ReadProperties and WriteProperties events. This is discussed in more detail in "Understanding Control Lifetime and Key Events," in "Building ActiveX Controls."
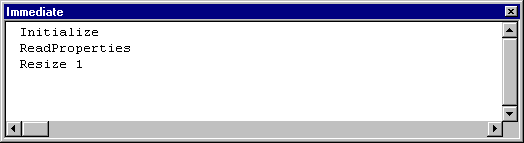
Whatís going on here? You havenít put another instance of the ShapeLabel control on Form1. Where did all these events come from?
This illustrates an important point about controls. A user puts a control on a form, and thereafter thinks of the control as a permanent fixture of the form. From the control authorís perspective, however, controls are getting destroyed and re-created all the time.
When you put ShapeLabel in run mode by closing its designer, the instance of ShapeLabel on Form1 was destroyed and re-created, at which point it received an Initialize event. Why didnít you see a Terminate event first? Because the original instance of ShapeLabel you placed on Form1 was created before you added the code in the UserControl_Terminate event procedure! Welcome to the wild and woolly world of control creation.
Note Control instances are also destroyed and recreated when you click Update UserControls on the formís context menu.
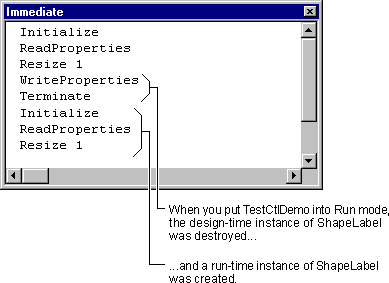
After a control instance is created, the ReadProperties event gives you a chance to obtain the controlís saved property values from the .frm file belonging to the form that contains the control instance.
When the design-time instance of the control is destroyed, the WriteProperties event gives you a chance to save the property values set at design time by the developer who's using your control. Property values are saved in the containing formís .frm file, as youíll see in "Saving the ShapeLabel Control's Property Values," later in this chapter.
The Terminate event occurs when the control is being destroyed.
Note By default, the Compile On Demand option is checked on the General tab of the Options dialog box (accessed from the Tools menu). Using CTRL+F5 (or Start with Full Compile, on the Run menu) overrides Compile On Demand, and fully compiles all the projects in the group before entering run mode. This is useful because compile errors usually require resetting the project, which means returning to design mode. When youíre debugging controls, you may prefer to turn Compile On Demand off rather than remembering to use CTRL+f5.
The run-time instance of a control never gets a WriteProperties event, because it doesnít need to save its property values. To see why not, consider ShapeLabelís future. When itís compiled into an .ocx file, youíll add it to another project, put an instance on a form, compile the project into an .exe, and run it. When you close that .exe, the only place the ShapeLabel instance could save its property values would be in the .exe file. This sort of behavior is not tolerated by well-behaved operating systems.

When a new instance of your control is placed on a container, it gets an InitProperties event. In the UserControl_InitProperties event procedure you can place code to:
-
Set the default values for each of the controlís properties values
- Perform tasks whenever a user creates an instance of your control.