Data Binding
See Also Tasks
Because of the interaction between browser, Web server, and database, accessing a database with Web pages is different than working with a database in a traditional application. Moreover, the process is different for server-based and client-based database access.
As explained later, if you use Visual InterDev tools to design database access for your application, you, as an application developer, will not need to worry about the underlying differences. Nonetheless, it is helpful to understand the following concepts:
Server Access to Databases
In server-based database access, the interaction between database and user shares some features with ordinary client-server database applications. However, the Web server sits between the two and introduces a layer of interaction with its own features.
The following characteristics dictate how the browser, Web server, and database server interact:
-
The client (the browser, which presents data entry forms and reports) has no direct connection to the database. The client can only transmit requests to the Web server, which then passes them to and from the database.
-
The database fulfills requests by sending recordsets to the Web server. The database server itself does not maintain recordsets, and by extension, does not track the current record in the recordset.
-
Interaction with the database is handled by server scripts, not by client scripts. Server scripts are processed before a page is sent to the browser, so that when a user interacts with the page (by clicking a button, for example), all database access for that page has already been accomplished.
-
The browser and the server are not in continual contact. The server does not maintain information about previous browser requests. For example, a server does not keep information about what record in a database the browser last requested.
As a result, interactions between users and databases in Web applications are handled differently than in traditional applications. For example, a common scenario is that the user sees a form containing database information and wants to page back and forth between records.
A typical sequence of events required to accomplish this task is something like this:
-
The user requests a page that contains the form.
-
When the server processes the page, it executes script that connects to the database, and then executes a query or stored procedure that returns one or more records.
-
The server script moves to one particular record out of the recordset.
-
The server script extracts data from the current record and writes the data into the Web page as HTML text. Information about the location of the current record, such as a bookmark or primary key, is stored in a global server variable or packaged up to be sent to the browser along with the page. Typically, the server then discards the recordset.
-
The server sends the page to the browser, where the user sees the database record in an HTML form.
-
The user clicks a "Next" button on the page. The button's script submits the HTML form to the server. Because the server has no connection to the browser, the button script must pass an indication to the server that the user is navigating to the next record. If the location of the current record was sent to the browser earlier, the browser sends that information back to the server.
-
At the server, server script parses the user's submission. In this case, the server detects that the user wants to navigate. The server then re-issues the earlier query, which returns a new recordset. The server uses the bookmark or primary key saved earlier to navigate to the correct place in the recordset, and then moves one record forward and repeats steps 4 and 5.
The scenario seems complicated because in effect the Web server forgets about both the recordset and the user's state as soon as it sends the page to the browser. As an analogy, the process is like having a telephone conversation with a friend in which you hang up after each sentence. Each time you dial and reconnect, your friend has forgotten everything you've said.
It is possible to cache recordsets so that the query does not have to be repeated each time. However, when browsing large amounts of data, caching is not recommended. If you do cache, even a small number of users could easily overwhelm the server's resources. However, if the recordset contains only a single row and you are going to update it using an optimistic lock, it can be efficient to cache the recordset on the server.
With server access to the database, the client environment has no direct control over database access. When the server extracts information from the recordset and writes it into the page, the information becomes indistinguishable to client scripts from ordinary HTML text. Client scripts cannot directly execute a command to move in the database. Instead, the client scripts must send sufficient information to a server script so that the server script can pick up where it left off in the data.
Note You can use design-time controls and the Visual InterDev scripting object model to create applications to make the process of handling user requests on the server transparent. For details, see Scripting with Design-Time Controls and Script Objects and Design-Time Controls.
Client Access to Databases
If your deployment environment makes it practical, you can create direct database access from the client to the database. You can then manage database access entirely from client scripts, which often results in faster database access. In addition, the development environment allows you to create a richer user experience by taking advantage of browser features.
To access a database from the client, you use features of Dynamic HTML specific to Microsoft® Internet Explorer 4.0. All your users must have Internet Explorer 4.0 as their browser. In addition, you must keep your database on a server that supports the correct data access software, or at least use a properly-configured server as a gateway to your database.
When you use client access to databases, the underlying interaction between application and database is simpler than that in server access. (If you use Visual InterDev tools to manage database access, the differences are invisible and the way you script for database access is the same for both types.)
To accomplish the navigation scenario described earlier under Server Access to Databases, the application follows these steps:
-
The user requests a page that contains the form.
-
The Web server passes the page to the browser. (If necessary, the server processes scripts on the page first, but server script is not required for database access.)
-
When the browser receives the page, an RDS (Remote Data Service) control on the page automatically opens the recordset and binds the data to the controls via the DHTML 4.0 data binding specifications.
-
The user clicks a "Next" button on the page. The button's script navigates to the next record in the recordset.
An important difference is that after the Web server has sent the page to the browser, the application does not require further requests to the server to manage database access, reducing substantially the number of browser-Web server round trips. In addition, because the client can cache the recordset, database actions such as navigation do not require that the recordset be regenerated. Finally, updates can be sent in batches for greater efficiency.
In all cases, the result is faster database access. You can create client-based database access using Microsoft Remote Data Service (RDS). For information about RDS, see the Microsoft RDS Web site at http://www.microsoft.com/data/rds/.
Data-Bound Controls and the Script Object Model
Although you are not required to use Visual InterDev data-bound controls for database access in your Web application, they greatly simplify application development. Data-bound controls provide a complete set of user interface elements, and in addition include all the logic necessary to connect to, navigate in, and update recordsets.
Data-bound controls include:
-
Recordset. Acts as the master control by binding to a database object. Other controls on the page in turn are bound to a recordset control.
-
Individual controls. Display the contents of a single field in a database record, including text boxes, list boxes, check boxes, radio buttons, and labels.
-
Grid. Displays a set of records.
-
RecordsetNavBar. Includes buttons that allow navigation to the next, previous, first, and last record in a result set.
In addition to making it easy to add user interface elements for database, the data-bound design-time controls can take advantage of the Visual InterDev scripting object model. This object model accomplishes two tasks. First, it provides a consistent interface for scripting database access, regardless of what type of database you are working with or whether you are scripting server or client access to databases. Second, it creates a high-level model for database access and manipulation, hiding from you most of the complexity involved in Web-based database access.
When working with data-bound controls, you work primarily with the Recordset control, which uses the scripting object model to expose properties and methods that help you manage the records in a result set. For example, to navigate between records in a result set, you can call a moveNext or movePrevious method of the Recordset object. The individual data-bound controls likewise expose properties and methods that bind them to the Recordset control and that determine the controls' appearance and behavior.
For more information about working with controls and the scripting object model, see Viewing Data and The Scripting Object Model.
Database Access Design in Visual InterDev Applications
Regardless of what database you want to access, Visual InterDev includes tools that greatly simplify the process. This section provides an overview of how you create a Web application with a database component, highlighting where you can take advantage along the way of Visual InterDev features.
Although the underlying process is different for server-based and client-based database access, the Visual InterDev database tools make the difference transparent. With only a few differences, you will be able to create both types of access using the same procedures.
In outline form, the steps required to set up a Web page with database access are as follows:
-
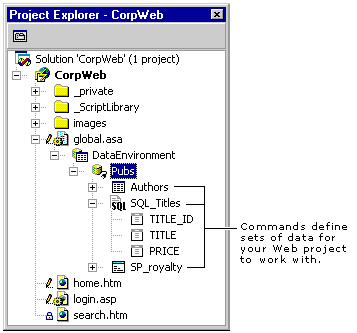
Establish a connection to a database. You specify a database to connect to by selecting Add Data Connection from the Project menu.
When you do, Visual InterDev creates a data environment, which acts as a repository for all data connection information in your project. Because different Web pages can share a data connection, scripts in the Global.asa file of your Web project maintain the data environment.

If your application requires access to more than one database (including databases on different servers), you can establish multiple connections in the data environment.
-
Define the data to use. For each connection in the data environment, you create one or more commands, which are objects that encapsulate references to SQL statements, stored procedures, tables, views, or synonyms. Each command produces a different result set (which is also called a cursor). For example, if your application reads data from a table, a query, and a stored procedure, you can define three different commands.
-
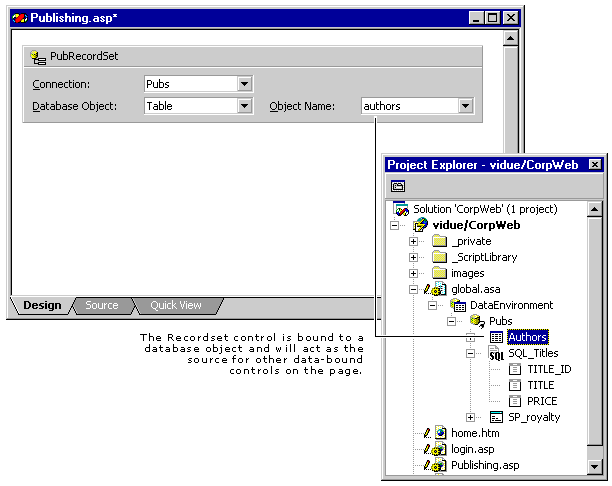
Add a Recordset control to your Web page. On the Web page where you want to use database data, you add a Recordset control. This control acts as the local controller when the page is running, providing an object for other data-bound controls to interact with. It is bound to database objects either directly or by using command objects in the data environment.
-
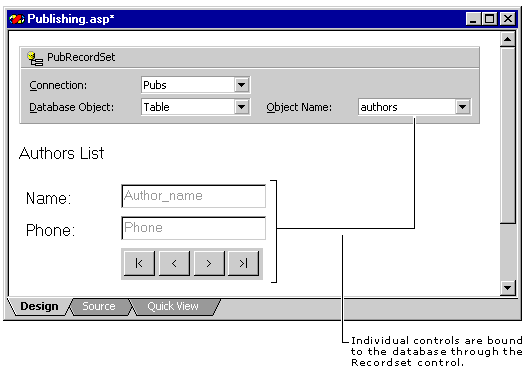
Add data-bound controls to your Web page. On the Web page where you have put the Recordset control, you add data-bound controls such as text boxes, check boxes, and buttons, as well as a navigation bar. You use these data-bound controls to define data entry forms, reports, or other user interface elements for the data in the database. Each data-bound control is linked to a field in a database via the Recordset control.
-
Add your own script. If the data-bound controls do not provide you with the full database interaction that you want in your application, you can write additional script. For example, you can write script that validates the user's entry into a data-bound text control. You can also write script to perform functions such as updating, adding, or deleting records by calling methods in the Recordset object. Finally, you can write script that executes database commands directly by referencing the commands stored in the data environment.
The scenario listed in the steps above is simple, but even complex scenarios do not require substantially greater effort. For example, a Web page for a catalog application might include a drop-down combo box that customers can select a product from. The drop-down list would be produced by a second recordset (in addition to the recordset being updated by the catalog page itself). The data access tools in Visual InterDev allow you to easily maintain both of these recordsets and likewise make it easy to bind specific controls to each set.
If you want, you can also bypass the data-bound controls and create your own database access in script. In that case, you would still use the data environment to establish connections and commands. The data environment presents an object model that you can interact with using script in order to query the database and modify it. For details, see Executing Database Commands Using the Data Environment.



