Microsoft Corporation
Updated April 1999
Summary: The Microsoft® Windows® Scripting Host (WSH) is a language-independent scripting host for 32-bit Windows platforms. Windows Scripting Host will be integrated into updates and new releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system. (7 printed pages)
The Microsoft® Windows® Scripting Host (WSH) is a language-independent scripting host for 32-bit Microsoft Windows operating system platforms. Microsoft provides both Visual Basic® Script and Java Script scripting engines with WSH. Microsoft anticipates that other software companies will provide ActiveX® scripting engines for other languages, such as Perl, TCL, REXX, and Python.
WSH can be run from either the Windows-based host (Wscript.exe) or the command shell–based host (Cscript.exe).
This article describes:
Windows Scripting Host is integrated into Windows 98, Internet Information Services version 4.0, Windows 2000 Server, and Windows 2000 Professional. It is also available for the Windows 95 operating system.
Windows Scripting Host (WSH ) brings simple, powerful, and flexible scripting to the 32-bit Windows platform.
Previously, the only native scripting language supported by the Windows operating system was the MS-DOS® command language. Although it is fast and small, MS-DOS has limited features, compared to Visual Basic Script and Java Script. Today, ActiveX scripting architecture allows users to take advantage of powerful scripting languages, such as Visual Basic Script and Java Script; and MS-DOS command scripts are still supported.
ActiveX scripting architecture enables powerful scripting, using languages such as VB Script, Java Script, and Perl. Microsoft currently provides three hosts for running these scripting languages across the Windows platform:
Internet Explorer enables scripts to be executed on client computers from within HTML pages.
Internet Information Services now supports Active Server Pages, which enable scripts to be run on Web servers; in other words, it enables server-side scripting over the Internet or an intranet.
Windows Scripting Host enables scripts to be executed directly on the Windows desktop or command console, without the need to embed those scripts in an HTML document. Scripts can be run directly from the desktop by clicking on a script file, or from the command console. WSH provides a low-memory scripting host that is ideal for non-interactive scripting needs, such as logon scripting, administrative scripting, and so on.
You must install Microsoft Internet Explorer version 3.0 or later to use Windows Scripting Host. WSH relies on the Visual Basic Script and Java Script engines provided with Internet Explorer 3.0 or later. WSH is installed as part of Windows 98, Windows 2000, and Internet Information Services 4.0. A separate setup program is provided for Windows 95.
To install WSH on a Windows 95–based system, install Microsoft Internet Explorer version 3.0 or later if you have not already done so. If you do not have Internet Explorer 3.0 or later, see the Microsoft IE Web page at www.microsoft.com/windows/ie/.
Download the WSH setup program from the Microsoft download site at www.microsoft.com/msdownload/vbscript/scripting.asp.
Cscript.exe uses the following syntax:
cscript [host options…] [script name] [script options]
Each parameter is optional; however, you cannot specify script parameters without specifying a script. If you do not specify parameters, Cscript.exe displays the Cscript.exe syntax and the valid host parameters.
Cscript.exe supports the following host parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
| //R | Reregister script extensions (.vbs, .js, .tcl) by searching for registered script engines. Note You do not need to provide a script file name when using the //R switch. |
| //I | Interactive mode (Default—Opposite of //B) |
| //B | Batch mode. Suppress all non-command-line console UI requested from script. |
| //T:nn | Time-out, in seconds. Maximum time the script can run (Default = No limit).
This option is used to prevent excessive execution of scripts; it sets a timer. When execution time exceeds the specified value, Cscript interrupts the script engine, using the IActiveScript::InterruptThread method and terminates the process. Note There is a callback hook. If the time-out is invoked, the OnTimeOut function is called to permit some cleanup. Although it is possible to create infinite loops, using this feature, it is more useful than harmful. |
| //logo | Display an execution banner at execution time (Default—Opposite of //NoLogo). |
| //nologo | Prevent display of execution banner at execution time. |
| //C | Make Cscript.exe the default application for running scripts. |
| //S | Save current command-line options for this user (per user). |
| //? | Show command usage (same as execution with no parameters). |
Several sample scripts are installed when you install WSH. The sample scripts are in the %windir%\WSamples folder (where %windir% is your Windows 95 or Windows 2000 folder).
cscript //logo %windir%\wsamples\chart.vbs
cscript //nologo %windir%\wsamples\chart.vbs
There are three ways to run scripts under windows, using WSH. You can:
When you run scripts from Wscript.exe, you can select the Always Use the Windows Scripting Host to open this file check box and set properties on the WSH Properties page.
When you run a script and the Always Use the Windows Scripting Host to open this file check box is selected, Wscript.exe is registered as the default application to run files with the extension of the script you are running. For example, if you select the check box when you run Chart.vbs, Wscript.exe becomes the default application for all files with the .vbs extension. This check box functions identically to the Cscript.exe //C switch.
The WSH Properties page provides the following options:
| Property | Use to… | CSCRIPT.EXE equivalent |
| Register common script extensions | Re-register the well-known script extensions (.vbs, .js, .tcl, ) by searching for well known registered script engines. | //R |
| Stop script after n seconds | Specify a maximum number of seconds that a script may run. (The default is no limit.) | //T:nn |
| By default, run scripts in the following mode: Interactive/Batch |
Suppress or enable all non-command-line console UI requests from the script. Interactive allows non-command-line console UI requests. Batch does not. | //I & //B |
The Windows Scripting Host serves as a controller of ActiveX scripting engines, just as Microsoft Internet Explorer does. Because the scripting host is not a full Internet browser, it has smaller memory demands than Microsoft Internet Explorer; therefore, WSH is appropriate for performing simple, quick tasks.
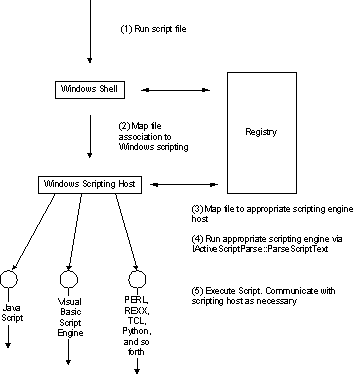
The scripting host reads and passes the specified script file contents to the registered script engine by the IActiveScriptParse::ParseScriptText method provided by the script engine. See the illustration in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Diagram of flow from scripting host to registered script engine
The scripting engine does not use the SCRIPT tag (used in HTML); instead, it relies on the extension of the file. Therefore, the script writer does not have to be familiar with the exact ProgID of various script engines. The scripting host maintains a mapping of the script extensions to ProgIDs and uses the Windows association model to launch the appropriate engine.
For the latest information on Windows 2000 Server, visit the Web site at www.microsoft.com/windows2000/guide/server/overview/default.asp or the Windows 2000 Server Forum on the Microsoft Network (GO WORD: MSNTS).
For the latest information on Windows scripting technology, visit the Microsoft Developer Network at http://msdn.microsoft.com/default.asp.
--------------------------------------------
The information contained in this document represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation on the issues discussed as of the date of publication. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information presented after the date of publication.
This article is for informational purposes only. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, IN THIS DOCUMENT.
The BackOffice logo, ActiveX, Visual Basic, Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other product or company names mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Microsoft Corporation · One Microsoft Way · Redmond, WA 98052-6399 · USA