You use discovery scope to determine the specific type of information you want Network Discovery to gather about the resources in your network. To specify this information, you enable and configure a combination of discovery types in the tabs of the Network Discovery Properties dialog box. When Network Discovery searches for system resources, it processes these combined options in parallel to gather the required information. You use the following tabs to configure discovery scope:
The information returned by Network Discovery corresponds to the type of discovery you enable in each of these tabs. Each discovery type provides unique information. For example, Domain, SNMP, and DHCP discovery find computers. In addition, SNMP finds gateways. Some discovery types discover IP addresses, some discover subnet masks, and some discover MAC addresses. Network Discovery correlates the information it gathers into a single DDR for each discovered resource.
By default, Network Discovery attempts to discover the subnet in which the SMS site server conducting the discovery resides (the local subnet). You can disable this feature in the Subnets tab. You can also specify other subnets you want to discover by specifying the subnet IP address and mask and then enabling it.
In the Subnets tab, Network Discovery lists the subnets it found during each previous discovery and marks them with a lock icon to indicate they cannot be modified or deleted. From this list, you can enable the subnets you want discovered during the next session and select each subnet independently, giving you full control over which ones are discovered. You cannot, however, delete or modify the subnets that Network Discovery finds and lists.
You cannot view the properties of any subnets that Network Discovery finds and lists. You can only view the properties of subnets that you enter manually. After Network Discovery discovers them, however, you can no longer change their properties.
If your SMS site server has multiple network interface cards (NICs), a subnet appears for each card.
In order to discover routers on the local subnet, Network Discovery uses the Router Information Protocol (RIP) and SNMP and listens for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) multicast addresses. Network cards generally support the filtering of multicast addresses, and the operating system will register with them when an application registers with Winsock. If an application fails to register because the network card cannot support any more multicast filters, the operating system should clear out the filters, register for all multicast addresses, and perform the filtering itself. Therefore, in cases where there are no more slots on a network card, Network Discovery cannot use OSPF; and as a result, the router will only be discovered if it has SNMP enabled.
By default, Network Discovery attempts to enumerate the computers on the local domain. You can disable this feature in the Domains tab. You can also specify additional domains you want discovered. You can discover the same domains by using the Domains tab that you can discover by using your site server to browse your Network Neighborhood. However, you must enter each domain you want discovered.
If you run Network Discovery with all options disabled, except the Domains tab, and you have selected the Topology, Client, and Operating System discovery type, Network Discovery will not be able to create a DDR for the computers it finds. If there is no DDR stored in the SMS site database for a specific Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 computer, Windows Remote Client Installation cannot install SMS Client software on it. If you plan to use both Network Discovery and Windows Remote Client Installation to install clients, make sure that you also configure one or more of the DHCP, SNMP, or Subnet tabs, as well as the Domains tab.
By default, Network Discovery attempts to contact the local router (default gateway) during topology discovery. It will retrieve data and the IP address from each device. Network Discovery uses this information to create an image of the network topology. You can also specify additional SNMP devices you want discovered in the SNMP Devices tab.
In order to gather data from SNMP devices, you must specify the SNMP community names that Network Discovery can use to access them. Each community name must have at least read access to some of the devices you want to discover. By default, Network Discovery uses the SNMP default community name, “public.” You can specify multiple community names that Network Discovery can use to access SNMP-enabled devices. Network Discovery will cycle through all of the listed names until one can be used successfully. If none are successful, it will abandon the attempt on that device. If your SMS site server has multiple NICs, Network Discovery will attempt to connect to all of the local SNMP devices.
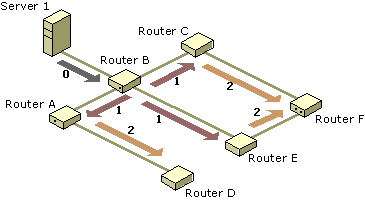
The hop count limit specified in the SNMP tab allows you to limit the number of routers from the default gateway that Network Discovery tries to discover. If it is set to 0, Network Discovery will only search the default gateway. If it is set to 1, Network Discovery will attempt to contact any other routers that are connected to the default gateway.
Figure 8.4 illustrates the router hop count process. Each time you increment the hop count, you extend the discovery to another set of gateways. Incrementing the hop count can be a very effective method of enabling discovery for major portions or even all of your network.

Figure 8.4 Router hop count
DHCP is a TCP/IP protocol used for assigning IP addresses to computers. DHCP discovery is enabled by default. You can configure which Microsoft DHCP servers Network Discovery will gather data from by typing their IP addresses in the DHCP tab. If your site server is also a DHCP client, DHCP discovery is automatically enabled for its DHCP server. To prevent Network Discovery from discovering your site server’s DHCP server, disable the Use local DHCP servers option or ensure that your site server is not also a DHCP client.
The DHCP server managing this process stores:
The DHCP server uses its configuration information to determine which networks it is managing (including the subnet address, the subnet mask, and a description of the network). Network Discovery retrieves information from the DHCP server in the form of RPCs made directly to the database on the DHCP server.
Network Discovery can only gather information from Microsoft DHCP servers. Your site server will need user-level security access to retrieve database information from DHCP servers. In other words, the SMS Service account must be a domain user in the same domain as the DHCP server.
You use the Schedule tab to start Network Discovery. In the Schedule tab, you specify the date and time to start Network Discovery and the discovery duration. After you select a start time, Network Discovery will begin at the scheduled time. Duration indicates the maximum length of time the discovery will run.
If you are running Network Discovery on a large network and you want it to stop at a specific time even if it is not completely finished, the Duration options allow you to stop discovery by the appropriate time. When the scheduled discovery time arrives, Network Discovery will use the configuration you currently have set.
You cannot save specific configurations to work at specific times. You can, however, determine when you would like Network Discovery to start. You can specify several schedules if you want Network Discovery to occur at specific times, including a recurrence pattern that will cause Network Discovery to run at regular intervals. During Network Discovery, the configuration currently set in the combination of tabs will occur concurrently.