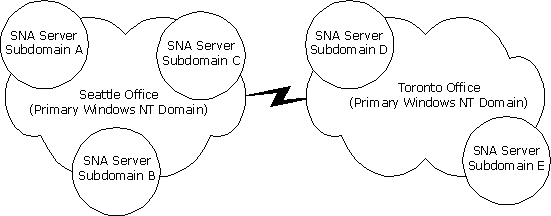

Figure 7.1 SNA Server subdomains can be located in geographically organized Windows NT domains.
The domain, as it pertains to Windows NT Server, is a group of computers that share a network resource database and have a common security policy. A Windows NT domain contains a primary domain controller (PDC) computer that acts as the resource and user manager for the entire domain. One or more computers in the domain may be configured to act as backup domain controllers (BDCs) that can take over for the PDC should any problems arise. The remaining computers in the domain are user workstations or servers that provide resources to domain users.
Within a Windows NT domain, SNA Server computers are logically grouped into entities called subdomains. Each SNA Server subdomain can contain up to 15 SNA Server computers, and a Windows NT domain may contain an unlimited number of subdomains.
In an enterprise, it is common to have multiple domains that manage user accounts independently of one another, as shown in Figure 7.1.
The domain model provides two key advantages over peer-to-peer networks with regards to security:
SNA Server relies on the PDC or BDC to provide authentication services to users requesting access to host resources. Only users who have been validated by the PDC or BDC can gain access to resources provided by servers in the subdomain.
Domain authentication is used to verify users who request resources provided by these services:
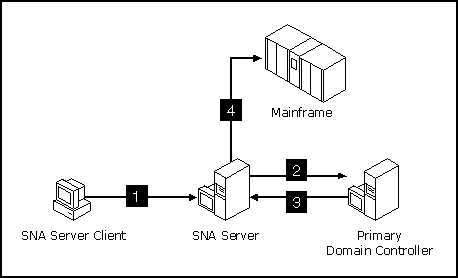
Figure 7.2 Domain authentication process for 3270 terminal access.
Each user who needs access to SNA Server resources must have a Windows NT domain account. Once enrolled as a Windows NT domain user, the individualís account is added to the SNA Server subdomain. After a user is added to the SNA Server subdomain, he or she can be allocated specific SNA resources.
Note Each computer running SNA Server also needs its own Windows NT domain account in which SNA Server services are run. SNA Server uses this account to log on to the domain to perform such functions as host printing and data encryption using the Distributed Link Services.