Most companies are turning to distributed computing and the Internet to provide users with fast access to information. Windows DNA is a framework for building a new generation of computing solutions that brings together the worlds of personal computing and the Internet. Windows DNA is the first application architecture that fully embraces and integrates both the Web and client/server models of application development.
By using the Windows DNA architecture, developers can build scalable, multitier business applications that can be delivered over any network, provide open access to diverse data sources across different platforms, and be freely accessed by any client computing platform. Windows DNA allows organizations to develop cross-platform applications that can access data sources on any server environment including Windows NT, Unix, and Systems Network Architecture (SNA)-based systems. By using Windows DNA architecture, organizations can capitalize on their existing technology infrastructure while also adopting new technologies (such as the Internet and World Wide Web) to meet new requirements.
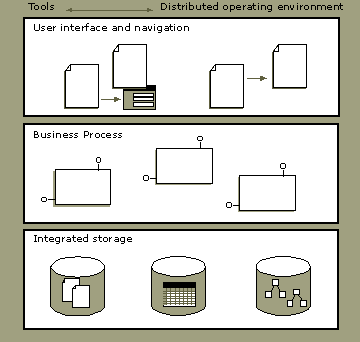
The Windows DNA architecture has three tiers:
This layer is the user interface plus basic validation code. Typically, this is a Web browser or a full-featured front-end client.
This layer, which includes middleware components and system services, handles application logic.
This layer is the database or another unstructured storage layer.

For more information about Microsoft Windows DNA, see www.microsoft.com/dna/.
In a mobile computing environment, the business process and integrated storage layers also must reside on the client. The Microsoft Component Object Model (COM) and Distributed COM (DCOM) components provide the foundation for component integration in a distributed environment. This offers several advantages when developing mobile applications:
Sybase Adaptive Server Anywhere 6.0 can participate in multitiered applications. However, heterogeneous joins are not supported without using Sybase OmniConnect.
Sybase Adaptive Server Anywhere 6.0 supports Java in the database engine. In theory, Java code that is written to run in the database server can be moved to run elsewhere. However, the code relies heavily on Java extensions that make sense only in the context of the database server. Moving the code to another location could break it.