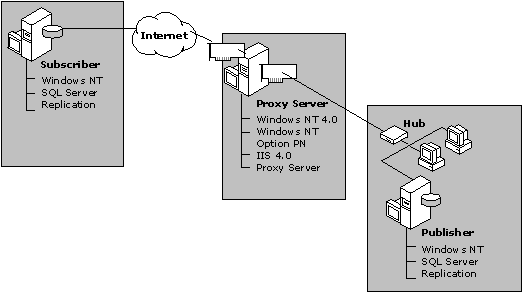
Configuring the network topology is the first step in defining how SQL Server and Microsoft Proxy Server will work together. As shown in the following illustration, Microsoft Proxy Server provides a gateway between the Internet and the internal network, which includes the server running SQL Server 7.0. The server running SQL Server is configured to be both a Publisher and a Distributor. A second server running SQL Server 7.0 and accessible on the Internet is configured as a pull Subscriber.

The software requirements for the proxy server are:
The software requirements for the server running SQL Server are:
The proxy server is configured as a multihomed server to prevent unauthorized users on the Internet from accessing the internal server running SQL Server.
A multihomed server is created by using two network interface cards (NICs). The first NIC, called the external proxy interface, isolates the Internet traffic from the internal network. The internal network is accessed through the second NIC, called the internal proxy interface.
This special Internet configuration does not affect the basic security properties of SQL Server. Users with appropriate permissions on the internal network can access data on SQL Server. Users on the Internet with appropriate permissions to SQL Server must have a valid account on the Proxy Server and be authenticated prior to gaining access to any data on SQL Server.
Do not specify a default gateway for the internal subnets of either the server running SQL Server or the proxy server. The default gateway of the external interface must point to its respective router's IP address.