 To create a relationship between major entities
To create a relationship between major entities
By establishing traits for the major entities, your model begins with several relationships. At this point, you can ask questions about things having traits, for example, “What authors have city Seattle?”, “Show authors and their cities,” “What book has the title The Busy Executive’s Database Guide?”, or “What publishers have country France?” But to ask the really interesting questions, you must create relationships between major entities, for example, “authors write books” and “publishers publish books.”
 To create a relationship between major entities
To create a relationship between major entities
If the relationship occurs at a time or place, including the time or place entity helps English Query answer some questions. The entities associated with the relationship “authors write books” might appear as shown in this illustration.
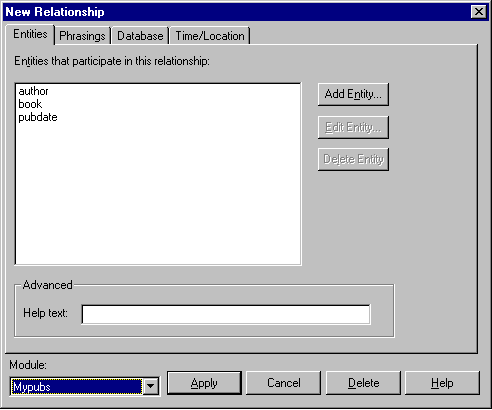
Next, you can create phrasings for the relationship. Phrasing types include verb phrasings (“authors write books”), preposition phrasings (“publishers are in cities”), adjective phrasings (“books are popular”), and subset phrasings (“some books are bestsellers”). Most trait phrasings (“books have royalties”) and name phrasings (“author names are the names of authors”) are created by Autotrait and Autoname.
This illustration shows the Verb Phrasing dialog box defined for “authors write books.”
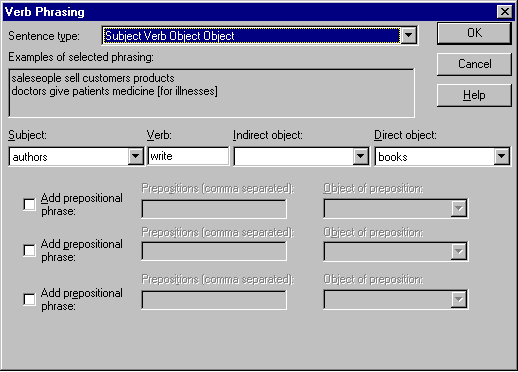
 To create phrasings for a relationship
To create phrasings for a relationship
If a relationship occurs at a specific time or place, then it is helpful to anticipate some user questions and to supply the date or location entity on the Time/Location tab of the New Relationship dialog box.
You can create relationships for every kind of question you want the user to ask. For example, if you want the model to support questions about authors in cities, return to the “authors have cities” relationship and supply a new preposition phrasing that says “authors are in cities.”