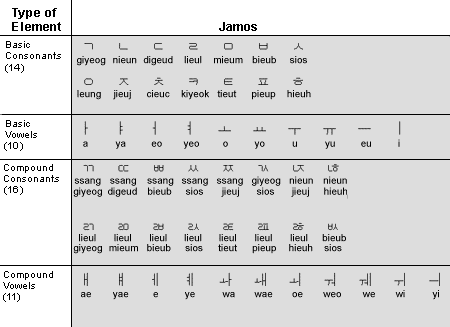
The Korean written language uses two types of characters: hangul and hanja. A hangul character is a single syllabic character created by combining one or more consonant signs and a vowel sign. There are 24 basic elements (14 consonants and 10 vowels), or phonemes, used to denote these signs; these elements are called jamos. You can create up to 51 jamos by combining two or more basic elements to form additional vowels or consonants, called compounds. Compounds and basic elements together comprise 21 vowels (10 basic vowels and 11 compound vowels) and 30 consonants (14 basic consonants and 16 compound consonants). Jamos are shown in Figure 7-4 below.

Figure 7-4 The elements of the Korean hangul writing system.
A hangul character (syllabic) consists of an initial consonant, a medial vowel, and sometimes a final consonant. Nineteen of the 30 consonants can be initial consonants. All 21 vowels can be medial vowels, and 27 of the 30 consonants can be final consonants. This means that 11,172 hangul character combinations are possible, though far fewer are actually used. The Wansung code page encodes the most common hangul character combinations, and the Johab code page covers all possible combinations. The Korean language also adopted hanja characters from Chinese and uses them for more formal written communication and to represent personal names. Most daily communications are written in hangul.